Metformin sensitizes triple-negative breast cancer to histone deacetylase inhibitors by targeting FGFR4
- PMID: 40091020
- PMCID: PMC11912690
- DOI: 10.1186/s12929-025-01129-7
Metformin sensitizes triple-negative breast cancer to histone deacetylase inhibitors by targeting FGFR4
Abstract
Background: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is characterized by high malignancy, strong invasiveness, and a propensity for distant metastasis, leading to poor prognosis and relatively limited treatment options. Metformin, as a first-line oral hypoglycemic agent, has garnered widespread research interest in recent years due to its potential in cancer prevention and treatment. However, its efficacy varies significantly across different tumor types. Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi), such as SAHA, have demonstrated antitumor activity, but TNBC responds poorly to HDACi monotherapy, possibly due to feedback activation of the JAK-STAT pathway. Exploring the synergistic potential and underlying mechanisms of combining metformin with HDACi in TNBC treatment is crucial.
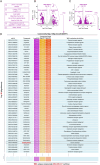
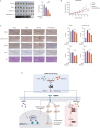
Methods: We predicted the synergistic effects of metformin and SAHA in TNBC using multiple computational methods (CMap, DTsyn, and DrugComb). We also developed a cancer-specific compound mimic library (CDTSL) and applied a three-step strategy to identify genes fitting the "metformin sensitization" model. Subsequently, we evaluated the synergistic effects of metformin and SAHA in TNBC cell lines through cell proliferation, colony formation, and apoptosis assays. Furthermore, we investigated the molecular mechanisms of the combined treatment using techniques such as transcriptome sequencing, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), Western blotting, and measurement of extracellular acidification rate (ECAR). Additionally, we assessed the in vivo antitumor effects of the combined therapy in a nude mouse subcutaneous xenograft model.
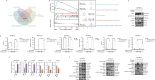
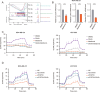
Results: CMap, DTsyn, and DrugComb all predicted the synergistic effects of SAHA and metformin in TNBC. The screening results revealed that HDAC10 played a key role in metformin sensitization. We found that the combination of metformin and SAHA exhibited synergistic antitumor effects (combination index CI < 0.9) in TNBC cell lines. Mechanistically, metformin inhibited histone acetylation on FGFR4, thereby blocking the feedback activation of FGFR4 downstream pathways induced by SAHA. Furthermore, metformin interfered with the glycolysis process induced by SAHA, altering the metabolic reprogramming of tumor cells. In in vivo experiments, the combined treatment of metformin and SAHA significantly inhibited the growth of subcutaneous tumors in nude mice.
Conclusions: Metformin enhances the sensitivity of TNBC to HDAC inhibitors by blocking the FGFR4 pathway and interfering with metabolic reprogramming. When used in combination with SAHA, metformin exhibits synergistic antitumor effects. Our study provides a theoretical basis for the combined application of HDAC inhibitors and metformin, potentially offering a new strategy for the treatment of TNBC.
Keywords: Drug synergism; Histone deacetylase inhibitors; Metformin; Triple-negative breast neoplasms.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study complied with all ethical regulations regarding animal experimentation. The use of animals was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Tongji University (Permit Number: SYXK 2020-0002). Consent for publication: All authors have consented to the publication of this manuscript. This manuscript does not contain data from any individual person; therefore, additional consent for publication is not required. Competing interests: No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- PDYLT2022-05/Pudong New Area Gynaecology and Obstetrics Medical Treatment Combination Project
- MOST2016YFC0900300/the Ministry of Science and Technology Fund
- 15410724000/the Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology Funds
- 15411953300/the Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology Funds
- 14ZR1429600/the Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology Funds
- 21ZR1451000/the Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology Funds
- 82002798/the National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Science Foundation Project
- 82102944/the National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Science Foundation Project
- 20204Y0131/the Shanghai Municipal Health Commission Project
- 20214Y0255/the Shanghai Municipal Health Commission Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

