Glycoside Hydrolase Family 16 Enzyme RsEG146 From Rhizoctonia solani AG1 IA Induces Cell Death and Triggers Defence Response in Nicotiana tabacum
- PMID: 40091519
- PMCID: PMC11911542
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.70075
Glycoside Hydrolase Family 16 Enzyme RsEG146 From Rhizoctonia solani AG1 IA Induces Cell Death and Triggers Defence Response in Nicotiana tabacum
Abstract
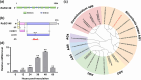
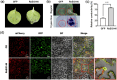
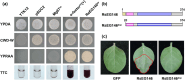
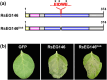
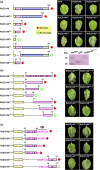
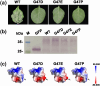
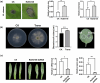
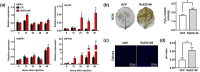
Rhizoctonia solani AG1 IA is a harmful necrotrophic fungus responsible for various crop diseases, including maize and rice sheath blight, which can lead to significant production losses. However, the pathogenic mechanisms and the roles of effectors in this pathogen remain poorly understood. In this study, we identified a glycoside hydrolase 16 family gene, RsEG146, from R. solani that was upregulated during its infection of Zea mays leaves. When transiently expressed through agroinfiltration, RsEG146 induced cell death in the leaves of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum 'Samsun'). The predicted signal peptide of RsEG146 was essential for its cell death-inducing activity, while the conserved enzymic active site was not required. The chitin-binding domain was critical for the cell death-inducing activity of RsEG146, with Gly47 identified as the key residue. Substitution of Gly47 with aspartate, glutamate, or proline significantly impaired the cell death-inducing activity of RsEG146. Additionally, transient and heterogeneous expression of RsEG146 enhanced the pathogenicity of Botrytis cinerea on tobacco, and silencing this gene through spray-induced gene silencing (SIGS) reduced the severity of the disease in maize, indicating that RsEG146 functions as an effector. Furthermore, RsEG146 triggered a plant immune response in tobacco. This study demonstrates that RsEG146 is a potential effector and plays a crucial role in the interactions between R. solani AG1 IA and its host.
Keywords: Rhizoctonia solani AG1 IA; cell death; glycoside hydrolase family 16; immune responses; spray‐induced gene silencing.
© 2025 The Author(s). Molecular Plant Pathology published by British Society for Plant Pathology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glycoside hydrolase 28 family protein RsPG1 from Rhizoctonia solani motivates immune response to pathogen attack in different host plants.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Jul;318(Pt 1):145008. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.145008. Epub 2025 Jun 6. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40484068
-
Identification and functional analysis of AG1-IA specific genes of Rhizoctonia solani.Curr Genet. 2014 Nov;60(4):327-41. doi: 10.1007/s00294-014-0438-x. Epub 2014 Jul 29. Curr Genet. 2014. PMID: 25070039
-
Transcriptome analysis reveals molecular mechanisms of sclerotial development in the rice sheath blight pathogen Rhizoctonia solani AG1-IA.Funct Integr Genomics. 2019 Sep;19(5):743-758. doi: 10.1007/s10142-019-00677-0. Epub 2019 May 3. Funct Integr Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31054140
-
Strategies to Manage Rice Sheath Blight: Lessons from Interactions between Rice and Rhizoctonia solani.Rice (N Y). 2021 Feb 25;14(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12284-021-00466-z. Rice (N Y). 2021. PMID: 33630178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tobacco leaf spot and root rot caused by Rhizoctonia solani Kühn.Mol Plant Pathol. 2011 Apr;12(3):209-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2010.00664.x. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Mol Plant Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21355993 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ainis, W. N. , Boire A., Solé‐Jamault V., Nicolas A., Bouhallab S., and Ipsen R.. 2019. “Contrasting Assemblies of Oppositely Charged Proteins.” Langmuir 35: 9923–9933. - PubMed
-
- Bacete, L. , Mélida H., Miedes E., and Molina A.. 2018. “Plant Cell Wall‐Mediated Immunity: Cell Wall Changes Trigger Disease Resistance Responses.” Plant Journal 93: 614–636. - PubMed
-
- Bernardes‐de‐Assis, J. , Storari M., Zala M., et al. 2009. “Genetic Structure of Populations of the Rice‐Infecting Pathogen Rhizoctonia solani AG‐1 IA From China.” Phytopathology 99: 1090–1099. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- 21KJD21003/the University Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province
- BE2022425/the R&D Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China
- BE2020319/Science and Technology Project of Jiangsu province, China
- XCX20240705/College students Science and Technology Innovation Fund of Yangzhou University
- CX(21)3096/the Fund for Independent Innovation of Agricultural Science in Jiang Province, China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

