Identification of lysosomal lipolysis as an essential noncanonical mediator of adipocyte fasting and cold-induced lipolysis
- PMID: 40091840
- PMCID: PMC11910232
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI185340
Identification of lysosomal lipolysis as an essential noncanonical mediator of adipocyte fasting and cold-induced lipolysis
Abstract
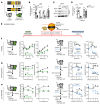
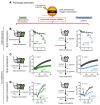
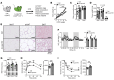
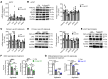
Adipose tissue lipolysis is the process by which triglycerides in lipid stores are hydrolyzed into free fatty acids (FFAs), serving as fuel during fasting or cold-induced thermogenesis. Although cytosolic lipases are considered the predominant mechanism of liberating FFAs, lipolysis also occurs in lysosomes via lysosomal acid lipase (LIPA), albeit with unclear roles in lipid storage and whole-body metabolism. We found that adipocyte LIPA expression increased in adipose tissue of mice when lipolysis was stimulated during fasting, cold exposure, or β-adrenergic agonism. This was functionally important, as inhibition of LIPA genetically or pharmacologically resulted in lower plasma FFAs under lipolytic conditions. Furthermore, adipocyte LIPA deficiency impaired thermogenesis and oxygen consumption and rendered mice susceptible to diet-induced obesity. Importantly, lysosomal lipolysis was independent of adipose triglyceride lipase, the rate-limiting enzyme of cytosolic lipolysis. Our data suggest a significant role for LIPA and lysosomal lipolysis in adipocyte lipid metabolism beyond classical cytosolic lipolysis.
Keywords: Adipose tissue; Endocrinology; Lysosomes; Metabolism; Obesity; Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL125838/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK133344/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL159461/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL146559/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL130028/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK131188/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL153047/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK132239/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL148280/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX003415/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 GM125944/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

