Epigenetic therapy sensitizes anti-PD-1 refractory head and neck cancers to immunotherapy rechallenge
- PMID: 40091844
- PMCID: PMC11910227
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI181671
Epigenetic therapy sensitizes anti-PD-1 refractory head and neck cancers to immunotherapy rechallenge
Abstract
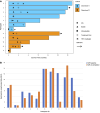
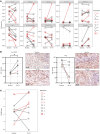
BACKGROUNDImmune checkpoint blockade (ICB) is an effective treatment in a subset of patients diagnosed with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC); however, the majority of patients are refractory.METHODSIn a nonrandomized, open-label Phase 1b clinical trial, participants with recurrent and/or metastatic (R/M) HNSCC were treated with low-dose 5-azacytidine (5-aza) daily for either 5 or 10 days in combination with durvalumab and tremelimumab after progression on ICB. The primary objective was to assess the biologically effective dose of 5-aza as determined by molecular changes in paired baseline and on-treatment tumor biopsies; the secondary objective was safety.RESULTSThirty-eight percent (3 of 8) of participants with evaluable paired tissue samples had a greater-than 2-fold increase from baseline in IFN-γ signature and CD274 (programmed cell death protein 1 ligand, PD-L1) expression within the tumor microenvironment (TME), which was associated with increased CD8+ T cell infiltration and decreased infiltration of CD4+ T regulatory cells. The mean neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) decreased by greater than 50%, from 14.2 (SD 22.6) to 6.9 (SD 5.2). Median overall survival (OS) was 16.3 months (95% CI 1.9, NA), 2-year OS rate was 24.7% (95% CI: 4.5%, 53.2%), and 58% (7 of 12) of treated participants demonstrated prolonged OS of greater than 12 months.CONCLUSIONOur findings suggest that low-dose 5-aza can reprogram systemic host immune responses and the local TME to increase IFN-γ and PD-L1 expression. The increased expression of these established biomarkers correlated with prolonged OS upon ICB rechallenge.TRIAL REGISTRATIONClinicalTrials.gov NCT03019003.FUNDINGNIH/NCI P01 CA240239.
Keywords: Cancer immunotherapy; Epigenetics; Head and neck cancer; Immunology; Oncology.
Figures





References
-
- Burtness B, et al. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2019;394(10212):1915–1928. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32591-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pai SI, et al. ICR gene signature to identify differential immune landscapes in anatomic subsites of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas and implications in personalized medicine. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(15):Suppl 6052. https://ascopubs.org/doi/10.1200/JCO.2018.36.15_suppl.6052. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

