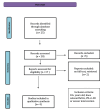
Impact of Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, and Sensor Technology in Knee Osteoarthritis Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 40092009
- PMCID: PMC11910998
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.79011
Impact of Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, and Sensor Technology in Knee Osteoarthritis Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) is a progressive degenerative joint disorder that significantly impacts mobility, pain levels, and overall quality of life. Conventional rehabilitation methods, while effective, often suffer from limitations related to patient adherence, accessibility, and cost. This systematic review examines the role of virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and sensor-based technologies in KOA rehabilitation, evaluating their effectiveness in pain reduction, functional improvement, and patient engagement. A comprehensive literature search identified four randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comprising 405 participants, with an average Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro) score of 6/10, indicating moderate to high methodological quality. Findings suggest that VR and AR interventions enhance rehabilitation adherence and engagement, while sensor-based systems provide real-time biofeedback, enabling personalized therapeutic adjustments. These technologies demonstrated significant improvements in pain management, muscle strength, and functional mobility. However, challenges such as high costs, limited accessibility, and the absence of standardized treatment protocols remain barriers to widespread clinical adoption. Further research should focus on long-term efficacy, cost-effectiveness, and the integration of these innovations into routine clinical practice.
Keywords: augmented reality; knee osteoarthritis; rehabilitation; sensor technology; virtual reality; wearables.
Copyright © 2025, Plavoukou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Effectiveness of Telerehabilitation in Managing Pain, Strength, and Balance in Adult Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis: Systematic Review.JMIR Rehabil Assist Technol. 2025 Apr 8;12:e72466. doi: 10.2196/72466. JMIR Rehabil Assist Technol. 2025. PMID: 40198917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, Gamification, and Telerehabilitation: Psychological Impact on Orthopedic Patients' Rehabilitation.J Clin Med. 2020 Aug 7;9(8):2567. doi: 10.3390/jcm9082567. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32784745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of virtual reality technology in postoperative rehabilitation following total knee arthroplasty: A scoping review.Int J Orthop Trauma Nurs. 2024 Aug;54:101124. doi: 10.1016/j.ijotn.2024.101124. Epub 2024 Jul 27. Int J Orthop Trauma Nurs. 2024. PMID: 39096627
-
Application of Virtual Reality-Assisted Exergaming on the Rehabilitation of Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2023 Nov 14;12(22):7091. doi: 10.3390/jcm12227091. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38002703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of virtual reality exercise in knee osteoarthritis rehabilitation: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Physiol. 2024 Jun 19;15:1424815. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1424815. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38962070 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Osteoarthritis: pathology, diagnosis, and treatment options. Abramoff B, Caldera FE. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32035570/ Med Clin North Am. 2020;104:293–311. - PubMed
-
- Telerehabilitation for patients with knee osteoarthritis: a focused review of technologies and teleservices. Naeemabadi Mr, Fazlali H, Najafi S, Dinesen B, Hansen J. https://biomedeng.jmir.org/2020/1/e16991 JMIR Biomed Eng. 2020;5:0.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials