Development and analytical performance of a new research use only (RUO) GP73 automated immunoassay
- PMID: 40092163
- PMCID: PMC11910086
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.101961
Development and analytical performance of a new research use only (RUO) GP73 automated immunoassay
Abstract
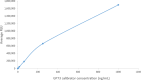
Golgi protein 73 (GP73) is a serum marker with potential applications in the assessment of chronic liver disease progression. We developed a research use only (RUO) GP73 immunoassay to detect serum GP73 concentration. A pair of internal antibodies that most effectively capture and detect GP73 were used to develop a prototype assay. An internal recombinant GP73 standard was used to prepare the assay calibrator and controls. The stability performance of the antibodies and GP73 calibrator were evaluated. We analyzed assay performance on the automated Alinity i system, including precision, sensitivity, linearity, endogenous interference, and HAMA/RF interference. The RUO Alinity i GP73 immunoassay showed good stability when the reagent kit was stored on board the instrument for more than 30 days without recalibration. The internal GP73 calibrator was stable at 2-8 °C for 28 days. Total %CV for 20 days was ≤3 %. The limit of quantitation (LoQ) at 20 % CV was 0.20 ng/mL or lower. Dilution analysis yielded a linear result within the range of 2.1 ng/mL - 1000.0 ng/mL. No interference was observed from common endogenous interferents at each test interference level. These findings support the reliability and robustness of the RUO Alinity i GP73 immunoassay for measuring serum GP73 concentration.
Keywords: Automated immunoassay; Biomarker; GP73; Hepatitis; Liver disease.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: All the authors are employees of Abbott Laboratories, which has developed the research use only, fully automated immunoassay for GP73 described in this manuscript. The development and performance evaluation of this assay, including the selection of antibodies, calibrators and controls, stability of the reagents, and analytical performance on the Alinity i system, were conducted as part of their employment. No other potential conflicts of interest were reported by the authors.
Figures
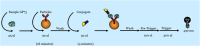






References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

