Assessing the quality of whole slide images in cytology from nuclei features
- PMID: 40092588
- PMCID: PMC11908589
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpi.2025.100420
Assessing the quality of whole slide images in cytology from nuclei features
Abstract
Background and objective: Implementation of machine learning and artificial intelligence algorithms into digital pathology laboratories faces several challenges, notably the variation in whole slide image preparation protocols. The diversity of preparation pipelines forces algorithms to be protocol-dependant. Moreover, the error susceptibility of each stage in the preparation process implies a need of quality control tools. To address these challenges, this article introduces a straightforward, interpretable, and computationally efficient quality control module to ensure optimal algorithmic performance.
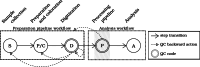
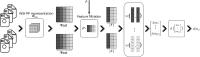
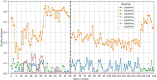
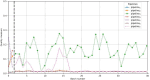
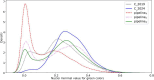
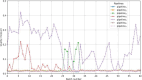
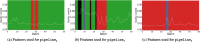
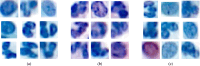
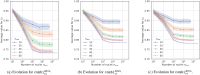
Methods: The proposed quality control module ensures algorithmic performance by representing an algorithm by a reference whole slide image preparation protocol validated on it. Then, inspired by data description methods, a preparation protocol is represented by nuclei feature distributions, obtained for several whole slide images it has produced. The quality of a preparation protocol is evaluated according to several reference preparation protocols, by comparing their feature distributions with a weighted distance.
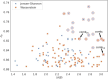
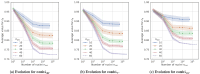
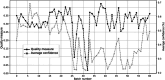
Results: Through empirical analysis conducted on seven distinct preparation protocols, we demonstrated that the proposed method build a quality module that clearly discriminates each preparation. Additionally, we showed that this module performs well on more larger and realistic corpus from laboratories routine, detecting quality deviations.
Conclusion: Even if the proposed method necessitates minimal data and few computational resources, we showed that it is interpretable and relevant on realistic corpus from several laboratories' routine. We strongly believe in the necessity of quality control from the algorithmic perspective and hope this kind of approach will be extended to improve quality and reliability of digital pathology whole slide images.
Keywords: Automated quality control; Cytology; Digital pathology; Out-of-distribution detection; Whole slide image analysis.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Paul Barthe, Romain Brixtel, Yann Caillot, Benoît Lemoine, Arnaud Renouf, Vianney Thurotte and Ouarda Beniken were employed at Datexim during this study.
Figures






References
-
- Ameisen D., Deroulers C., Perrier V., et al. Stack or trash? Quality assessment of virtual slides. Diagn Pathol. 2013;8:S23. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-8-S1-S23. - DOI
-
- Brixtel R., Bougleux S., Lézoray O., et al. Whole slide image quality in digital pathology: review and perspectives. IEEE Access. 2022;10:131005–131035. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3227437. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

