Efficacy of novel activated bamboo charcoal in reducing uremic toxins and enhancing kidney function in chronic kidney disease patients: a pilot randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 40093417
- PMCID: PMC11910151
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.19007
Efficacy of novel activated bamboo charcoal in reducing uremic toxins and enhancing kidney function in chronic kidney disease patients: a pilot randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: The role of uremic toxins in the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and novel treatments to mitigate their effects are critical areas of research. This pilot study investigated the efficacy of a novel activated bamboo charcoal and/or probiotics in reducing uremic toxins and improving renal function in CKD patients.
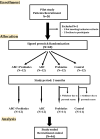
Methods: This prospective, randomized, open, blinded end-point (PROBE) study included patients with stage 3 CKD. Patients were randomly assigned to one of four groups: activated bamboo charcoal (ABC), probiotics, ABC with probiotics, or standard treatment for 3 months.
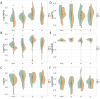
Results: A total of 46 patients were enrolled (mean age 66.7 ± 11.5 years, 71.7% male). The ABC and ABC with probiotics groups showed a significant reduction in serum levels of the uremic toxins trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), p-cresyl sulfate (PCS), indoxyl sulfate (IS), and phenyl sulfate (PS) after 3 months of treatment (all p < 0.05). There was a particularly pronounced decrease in the percentage of IS in both the ABC group (-23.9 ± 28.9% vs. 33.9 ± 63.4%, p = 0.005) and the ABC with probiotics group (-29.3 ± 30.6% vs. 33.9 ± 63.4%, p = 0.009). The eGFR change ratio also significantly improved in the ABC group compared to the control group (4.6 ± 10.2% vs. -8.6 ± 12.5%, p = 0.011). However, the probiotics group did not exhibit a similar reduction in uremic toxins or an improvement in the eGFR.
Conclusion: This study suggested that ABC significantly reduced uremic toxins and might have potential in improving eGFR in CKD stage 3 patients over a 3-month period. These findings suggest a potential protective effect of ABC on kidney function, highlighting the need for further large-scale, long-term randomized controlled trials to confirm these results.
Keywords: Activated bamboo charcoal; Chronic kidney disease; Indoxyl sulphate; Phenyl sulfate; Probiotics; TMAO; p-Cresyl sulfate.
©2025 Hung et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
CharXgen-Activated Bamboo Charcoal Encapsulated in Sodium Alginate Microsphere as the Absorbent of Uremic Toxins to Retard Kidney Function Deterioration.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 13;21(4):1257. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041257. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32070049 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in gut-derived uremic toxins before the onset of azotemic chronic kidney disease in cats.J Vet Intern Med. 2025 Jan-Feb;39(1):e17289. doi: 10.1111/jvim.17289. J Vet Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 39739435 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Sevelamer on Serum Levels of Gut-Derived Uremic Toxins: Results from In Vitro Experiments and A Multicenter, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Clinical Trial.Toxins (Basel). 2019 May 17;11(5):279. doi: 10.3390/toxins11050279. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31109001 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Protein-bound uremic toxin lowering strategies in chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Nephrol. 2021 Dec;34(6):1805-1817. doi: 10.1007/s40620-020-00955-2. Epub 2021 Jan 23. J Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33484425
-
Impacts of Indoxyl Sulfate and p-Cresol Sulfate on Chronic Kidney Disease and Mitigating Effects of AST-120.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Sep 11;10(9):367. doi: 10.3390/toxins10090367. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30208594 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akizawa T, Asano Y, Morita S, Wakita T, Onishi Y, Fukuhara S, Gejyo F, Matsuo S, Yorioka N, Kurokawa K, CAP-KD Study Group Effect of a carbonaceous oral adsorbent on the progression of CKD: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. American Journal of Kidney Diseases. 2009;54:459–467. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.05.011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barreto FC, Barreto DV, Liabeuf S, Meert N, Glorieux G, Temmar M, Choukroun G, Vanholder R, Massy ZA, European Uremic Toxin Work G Serum indoxyl sulfate is associated with vascular disease and mortalit y in chronic kidney disease patients. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 2009;4:1551–1558. doi: 10.2215/CJN.03980609. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Shi J, Ma X, Shi D, Qu H. Effects of microbiota-driven therapy on circulating indoxyl sulfate an d P-cresyl sulfate in patients with chronic kidney disease: a systemat ic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Advances in Nutrition. 2022;13:1267–1278. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmab149. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

