Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 2 H-[1,4]oxazino-[2,3- f]quinazolin derivatives as potential EGFR inhibitors for non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 40093516
- PMCID: PMC11907643
- DOI: 10.1039/d4md01016g
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 2 H-[1,4]oxazino-[2,3- f]quinazolin derivatives as potential EGFR inhibitors for non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
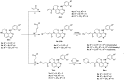
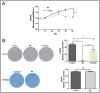
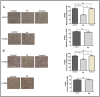
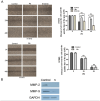
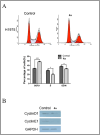
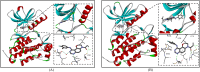
Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) have emerged as the first-line treatment for patients with EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). A series of 2H-[1,4]oxazino[2,3-f]quinazolin derivatives were synthesized and evaluated as irreversible EGFR-TKIs for the treatment of NSCLC. Most of the synthesized compounds demonstrated strong inhibitory activity against the EGFR kinase and the tested cancer cells. Notably, compound 4a exhibited considerable inhibitory effects against the EGFR kinase and the EGFRL858R/T790M mutant NCI-H1975 cancer cells. Compound 4a was found to suppress cell proliferation, colony formation, cell invasion, and migration, while also inducing G0/G1 phase arrest of the cell cycle in NCI-H1975 cells. Compound 4a was docked into the active pocket of the EGFR mutant to ascertain the probable binding conformation. Overall, compound 4a was identified as a promising irreversible EGFR-TKI for the treatment of NSCLC.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
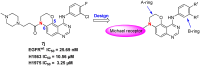
References
-
- Sung H. Ferlay J. Siegel R. L. Laversanne M. Soerjomataram I. Jemal A. Bray F. Ca-Cancer J. Clin. 2021;71:209. - PubMed
-
- Herbst R. S. Morgensztern D. Boshoff C. Nature. 2018;553:446. - PubMed
-
- Das D. Xie L. Wang J. Shi J. Hong J. Bioorg. Chem. 2020;99:103790. - PubMed
-
- Warnecke B. Nagasaka M. Adv. Oncol. 2024;4:63.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

