The Current Status, Hotspots, and Development Trends of Nanoemulsions: A Comprehensive Bibliometric Review
- PMID: 40093547
- PMCID: PMC11910037
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S502490
The Current Status, Hotspots, and Development Trends of Nanoemulsions: A Comprehensive Bibliometric Review
Abstract
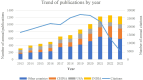
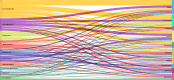
Nanoemulsions, which are characterized by their nanometer-scale droplets, have gained significant attention in different fields, such as medicine, food, cosmetics, and agriculture, because of their unique properties. With an increasing number of countries engaging in research on nanoemulsions, interest in their properties, preparation methods, and applications has increased. Hence, tracing the relevant research on nanoemulsions published in the past ten years on a global scale, by conducting data mining and visualization analysis on a sufficiently large text dataset through bibliometrics, sorting out and summarizing certain indicators, the development history, research status and research hotspots in the field of nanoemulsions can be clearly revealed, providing reference value and significance for subsequent research. This bibliometric review examines the research landscape of nanoemulsions from 2013-2023 via the SCI-E and SSCI databases, providing insights into the current status, hotspots, and future trends of this field. To offer a comprehensive overview, this analysis includes publication counts, author keywords, institutional contributions, research areas, prolific authors, highly cited papers and hot research papers. The findings reveal that China led in nanoemulsions research, followed by USA, India, and Brazil, with the University of Massachusetts emerging as a key player with the highest average number of citations per article (ACPP) and h-index. Food Chemistry, Pharmaceutics, and the Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology are among the top journals publishing in this area. Chemistry, pharmacology, and pharmacy emerged as the primary research domains, with McClements DJ as the most prolific and influential author. In keyword analysis, essential oil nanoemulsions are currently the main preparation direction, and various characteristics of nanoemulsions, such as their bioavailability, stability, biocompatibility, and antioxidant and antibacterial properties, have also been studied extensively. Research hotspots are focused mostly on the development of new applications and technologies for nanoemulsions.
Keywords: bibliometrics; bioavailability; drug delivery; essential oil; keyword analysis; nanoemulsions.
© 2025 Sun et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures




References
-
- Solans C, Izquierdo P, Nolla J, Azemar N, Garcia-Celma MJ. Nano-emulsions. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci. 2005;10(3–4):102–110. doi:10.1016/j.cocis.2005.06.004 - DOI
-
- Ozogul Y, Karsli GT, Durmus M, et al. Recent developments in industrial applications of nanoemulsions. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2022;304: 102685. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

