Mitigate or exacerbate? Assessing digital engagement's impact on mental health inequalities across gender and urban-rural divides
- PMID: 40093695
- PMCID: PMC11907620
- DOI: 10.1177/20552076251326673
Mitigate or exacerbate? Assessing digital engagement's impact on mental health inequalities across gender and urban-rural divides
Abstract
Objectives: Mental health inequalities have increasingly become an important factor affecting social well-being. Existing researches have focused on the impact of digital inequalities on mental health, but there is lack of research exploring the impact of digital engagement on mental health inequalities.
Methods: Based on data from the China Family Panel Studies (CFPS) wave 2020, this study analyzed the effects of digital engagement on adult mental health and mental health inequalities using multinomial OLS models and RIF models. Further, the mitigating effects of digital engagement on gender mental health inequalities and urban-rural mental health inequalities were calculated using RIF decomposition.
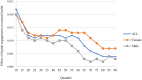
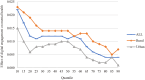
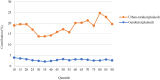
Results: Digital engagement positively predicts the mental health level of Chinese adults, and at the same time mitigates mental health inequalities among Chinese adults, including inequalities between genders and between urban and rural areas, and the mitigating effect on mental health inequalities is stronger between urban and rural areas. In addition, the mitigating effect of digital engagement on gender mental health inequalities diminished with increasing mental health levels; however, the mitigating effect of digital engagement on urban-rural mental health inequalities was stronger at low and high mental health levels.
Conclusions: Both gender mental health inequality and urban-rural mental health inequality are evident among Chinese adults. Digital engagement can alleviate overall mental health inequalities, including gender mental health inequalities and urban-rural mental health inequalities, while enhancing mental health. This provides new insights into how best to mitigate mental health inequalities in the digital era.
Keywords: Digital engagement; gender disparities; mental health inequalities; resource substitution theory; urban–rural disparities.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Sommet N, Morselli D, Spini D. Income inequality affects the psychological health of only the people facing scarcity. Psychol Sci 2018; 29: 1911–1921. - PubMed
-
- Kurtze N, Eikemo TA, Kamphuis CBM. Educational inequalities in general and mental health: differential contribution of physical activity, smoking, alcohol consumption and diet. Eur J Public Health 2013; 23: 223–229. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

