Interleukin 26 attenuates osteoblast differentiation in osteoarthritis patients by activating COX2 and NF-κB pathways
- PMID: 40093804
- PMCID: PMC11905269
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.102967
Interleukin 26 attenuates osteoblast differentiation in osteoarthritis patients by activating COX2 and NF-κB pathways
Abstract
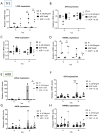
Aims: Osteoarthritis (OA) represents the prevailing form of degenerative joint pathology. Recent investigations have revealed a heightened expression of interleukin 26 (IL-26) in various inflammatory arthritic conditions, including OA. However, the specific impacts and functions of IL-26 on osteoblasts (OBs) within the context of OA remain inadequately elucidated. This study aims to clarify the effects and underlying mechanisms of IL-26 by examining its influence on osteoblasts isolated from OA patients and a murine osteoblast cell line. Methods: Human primary osteoblasts and mouse pre-osteoblast cells were subjected to treatment with β-glycerophosphate or concurrent treatment with IL-26 to observe the effects on osteoblast differentiation. The differentiation of osteoblasts was assessed through the expression of relevant genes using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Key molecular mechanisms of downstream signaling pathways were examined through immunoblotting assays. Results: Our results reveal that IL-26 mitigates osteoblast differentiation and reduces the expression of the marker alkaline phosphatase. Furthermore, the NF-κB downstream OB proliferated marker iNOS and inhibition OB differentiated marker LCN2 messenger RNA are up-regulated in IL-26 treated group. Also, phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 occur following IL-26 stimulation. Additionally, IL-26 enhances the downstream transcription factor cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2), a major player associated with iNOS. STAT1, the canonical receptor signaling pathway of IL-26 is activated. Conclusion: In summary, our findings substantiate the role of IL-26 in osteoarthritis and identify it as a potential therapeutic target for intervention in osteoarthritic pathology.
Keywords: interleukin 26; osteoarthritis; osteoblast differentiation.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures





References
-
- Kapoor M, Martel-Pelletier J, Lajeunesse D, Pelletier JP, Fahmi H. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7:33–42. - PubMed
-
- Le Henaff C, Mansouri R, Modrowski D, Zarka M, Geoffroy V, Marty C. et al. Increased NF-κB Activity and Decreased Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Mediate Reduced Osteoblast Differentiation and Function in ΔF508 Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) Mice. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:18009–17. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

