Neurochemical characteristics of pathological tissues in epilepsy: A preliminary 1H MR spectroscopy study at 7 T
- PMID: 40093876
- PMCID: PMC11910369
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejro.2025.100640
Neurochemical characteristics of pathological tissues in epilepsy: A preliminary 1H MR spectroscopy study at 7 T
Abstract
Background and purpose: This study aims to evaluate the neurochemical characteristics of pathological tissues by 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) in patient with pharmaco-resistant focal epilepsy at 7 T.
Methods: Thirteen patients with drug-resistant epilepsy and focal seizure successfully underwent MRS examinations at 7 T MRI scanners. 1H MR spectra were acquired from two voxels (lesion side and contralateral side) using the semi-adiabatic spin-echo full-intensity localized spectroscopy (sSPECIAL) sequence. Metabolite levels were quantified from LCModel and reported as to total creatine ratio.
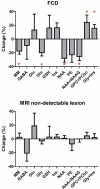
Results: In comparison to the contralateral side, lesions in focal cortical dysplasia demonstrated significantly reduced macromolecule and N-acetyl aspartate, significantly increased total choline and glycine + myo-inositol, and a distinct reduction trend of glutamate.
Conclusions: We conclude that performing MRS at high magnetic field offered the potential to reveal metabolic alterations in epilepsy lesions that may help to further understand the underlying pathophysiology of the disease.
Keywords: 7 T; Cortical dysplasia; Epilepsy; MR spectroscopy; Non lesional.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regional Myo-Inositol, Creatine, and Choline Levels Are Higher at Older Age and Scale Negatively with Visuospatial Working Memory: A Cross-Sectional Proton MR Spectroscopy Study at 7 Tesla on Normal Cognitive Ageing.J Neurosci. 2020 Oct 14;40(42):8149-8159. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2883-19.2020. Epub 2020 Sep 29. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32994337 Free PMC article.
-
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in focal cortical dysplasia at 3T.Seizure. 2015 Nov;32:23-9. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2015.08.008. Epub 2015 Aug 29. Seizure. 2015. PMID: 26552557
-
MR-spectroscopy in metachromatic leukodystrophy: A model free approach and clinical correlation.Neuroimage Clin. 2023;37:103296. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2022.103296. Epub 2022 Dec 20. Neuroimage Clin. 2023. PMID: 36563646 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic heterogeneity in different subtypes of malformations of cortical development causing epilepsy: a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Dec 1;13(12):8625-8640. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-552. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 38106257 Free PMC article.
-
Spectroscopic meta-analyses reveal novel metabolite profiles across methamphetamine and cocaine substance use disorder.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2023 Jul 1;248:109900. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2023.109900. Epub 2023 Apr 26. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2023. PMID: 37148676 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cendes F., Caramanos Z., Andermann F., Dubeau F., Arnold D.L. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging and magnetic resonance imaging volumetry in the lateralization of temporal lobe epilepsy: a series of 100 patients. Ann. Neurol. 1997;42(5):737–746. doi: 10.1002/ana.410420510. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

