Active microneedle patch equipped with spontaneous bubble generation for enhanced rheumatoid arthritis treatment
- PMID: 40093896
- PMCID: PMC11905133
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.103080
Active microneedle patch equipped with spontaneous bubble generation for enhanced rheumatoid arthritis treatment
Abstract
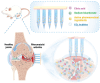
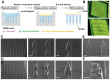
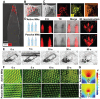
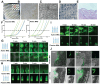
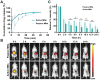
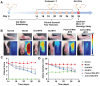
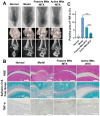
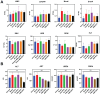
Rationale: The utilization of dissolving microneedles (MNs) facilitates the painless delivery of pharmaceuticals via the transdermal route. However, conventional MNs rely on passive diffusion through the gradual dissolving of the matrix, which can impede the therapeutic efficacy of the delivered drugs. Methods: In this study, we present the development of a novel degradable active MNs platform. This platform employs sodium bicarbonate and citric acid loaded in a dissolving MNs patch as a built-in motor for deeper and faster intradermal payload delivery. The sodium bicarbonate microparticles and citric acid undergo a chemical reaction when in contact with tissue fluid, resulting in the rapid formation of explosive carbon dioxide bubbles. This provides the necessary force to break through dermal barriers and enhance payload delivery. Results: The results demonstrated that the active MNs possessed excellent mechanical properties, rapid detachment characteristics, and superior drug release kinetics. Furthermore, the drug permeation behavior of active MNs exhibited enhanced permeation and distribution in skin-mimicking gel and porcine skin when compared to conventional passive MNs. In vivo experiments employing a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis showed that active MNs achieved superior therapeutic efficacy compared to passive MNs. Conclusions: This universal and effective autonomous dynamic microneedle delivery technology is straightforward to prepare and ultilize, and has the potential to improve the therapeutic efficacy of drugs, offering significant prospects for a diverse range of therapeutic applications.
Keywords: active microneedles; bubble generation; rapid separation; rheumatoid arthritis; transdermal drug delivery.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Liu T, Fu J, Chen M, Wu Q, Quan G, Wu C. et al. In situ polymeric nanomicelle-generating dissolving microneedle patch for enhanced transdermal methotrexate delivery in rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Eur Polym J. 2024;210:113008.
-
- Xie J, Zhu X, Wang M, Liu C, Ling G, Zhang P. Dissolving microneedle-mediated transdermal delivery of flurbiprofen axetil-loaded pH-responsive liposomes for arthritis treatment. Chem Eng J. 2024;482:148840.
-
- Nooreen R, Nene S, Jain H, Prasannanjaneyulu V, Chitlangya P, Otavi S. et al. Polymer nanotherapeutics: a versatile platform for effective rheumatoid arthritis therapy. J Control Release. 2022;348:397–419. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

