A simple cost-effective method for purification of Clostridium chauvoei cell-surface proteins for detection of antibodies against blackleg disease vaccine
- PMID: 40094060
- PMCID: PMC11905958
- DOI: 10.30466/vrf.2024.2023812.4190
A simple cost-effective method for purification of Clostridium chauvoei cell-surface proteins for detection of antibodies against blackleg disease vaccine
Abstract
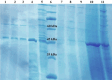
Cell-surface proteins of Clostridium chauvoei were purified using a simple method. Bacterial cultures were centrifuged and agitated vigorously in phosphate buffered saline with or without further glycine treatment and ammonium sulfate precipitation. Rabbits were immunized subcutaneously with a blackleg disease vaccine twice with a two-week interval. Immunized sera were collected one week after the second injection. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was performed using the proteins purified by the second method as the coating antigen. Bradford assay results showed a higher protein concentration in the second than the first method. Sodium dodecyl-sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis showed multiple bands for the cell-surface proteins of C. chauvoei in the first method and a sharp band equivalent to flagellin protein in the second method. The ELISA results indicated that the purified proteins were capable of detecting antibodies against Blackleg disease vaccine. The purified protein would be an alternative antigen for indirect ELISA in order to monitor the immune response in vaccinated farm animals.
Keywords: Clostridium septicum; ELISA; Flagellin; Glycine; Immunity.
© 2025 Urmia University. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Useh NM, Nok AJ, Esievo KA. Pathogenesis and pathology of blackleg in ruminants: the role of toxins and neuraminidase A short review. Vet Q. 2003;25(4):155. - PubMed
-
- Prescott JF. Brief description of animal pathogenic clostridia. In: Uzal FA, Songer G, Prescott JF, et al., editors. Clostridial diseases of animals. New Jersey, USA: Wiley-Blackwell ; 2016. pp. 13–19.
-
- Frey J, Johansson A, Bürki S, et al. Cytotoxin CctA, a major virulence factor of Clostridium chauvoei conferring protective immunity against myonecrosis. Vaccine. 2012;30(37):5500. - PubMed
-
- Nicholson P, Furrer J, Hässig M, et al. Production of neutralizing antibodies against the secreted Clostridium chauvoei toxin A (CctA) upon blackleg vaccination. Anaerobe. 2019;56:78–87. - PubMed
-
- Stevenson E, Minton NP, Kuehne SA. The role of flagella in Clostridium difficile pathogenicity. Trends Microbiol. 2015;23(5):275. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
