Predictors of Treatment Adherence in Kidney Transplant Patients: A Systematic Review of the Literature
- PMID: 40095588
- PMCID: PMC11900085
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14051622
Predictors of Treatment Adherence in Kidney Transplant Patients: A Systematic Review of the Literature
Abstract
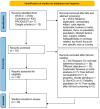
Background: Kidney transplantation (KTx) is a safe procedure that improves the life expectancy and quality of life of patients requiring it. However, despite the known benefits for patients who receive a kidney transplant, non-adherence to immunosuppressive medication is an unsolved problem, reflected mainly by graft rejection. Objective: The aim of this study is to systematically review the existing literature on adherence factors to medication after renal transplantation. Methods: A systematic literature review of studies published since 2010 was conducted in three databases. Records for the search were limited to publications from 2010 to 2024, available in full-text. The search was carried out in July 2024. In total, 2632 abstracts were downloaded from the different databases. Inclusion criteria were papers of any type (quantitative or qualitative) whose objective was the identification of predictors of adherence for patients who were prescribed immunosuppressive medication after kidney transplantation. Results: The predictors of adherence to treatment found in the systematic review were grouped into the following categories of the World Health Organization classification: socio-economic factors, factors related to the treatment/therapy, patient-related factors, disease-related factors, and health care system factors. Most of the studies were excluded, and in the end, 30 were included in the final analysis. According to these studies, a set of strong predictors was identified, but discrepancies among the variables of gender in young patients, pre-emptive transplantation, and the time of the transplantation were detected. Conclusions: In this study, we identified specific predictors and directions for the association of those predictors with adherence to immunosuppressive medication for patients after KTx. Further research should consider conducting reviews for different patient sub-groups on medication adherence and the development and validation of a screening instrument for adherence/non-adherence factors that clinicians could use as a detection tool for subjects at risk of low adherence.
Keywords: adherence; immunosuppressive medication; kidney transplantation; systematic literature review.
Conflict of interest statement
Some of the authors of this article declare financial conflicts of interest due to received honoraria and consulting fees and working as a speaker in projects promoted by pharmaceutical companies.
References
-
- Lemoine M., Titeca Beauport D., Lobbedez T., Choukroun G., Hurault de Ligny B., Hazzan M., Guerrot D., Bertrand D. Risk Factors for Early Graft Failure and Death After Kidney Transplantation in Recipients Older Than 70 Years. Kidney Int. Rep. 2019;4:656–666. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2019.01.014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eurotransplant Eurotransplant Annual Report 2021 2021. [(accessed on 21 February 2025)]. Available online: https://www.eurotransplant.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/ETP_AR2023_Low....
-
- Saran R., Robinson B., Abbott K.C., Agodoa L.Y.C., Albertus P., Ayanian J., Balkrishnan R., Bragg-Gresham J., Cao J., Chen J.L.T., et al. US Renal Data System 2016 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017;69:A7–A8. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2016.12.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed