Patient-Self Inflicted Lung Injury (P-SILI): An Insight into the Pathophysiology of Lung Injury and Management
- PMID: 40095610
- PMCID: PMC11900086
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14051632
Patient-Self Inflicted Lung Injury (P-SILI): An Insight into the Pathophysiology of Lung Injury and Management
Abstract
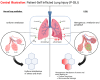
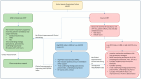
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a heterogeneous group of disease entities that are associated with acute hypoxic respiratory failure and significant morbidity and mortality. With a better understanding and phenotyping of lung injury, novel pathophysiologic mechanisms demonstrate the impact of a patient's excessive spontaneous breathing effort on perpetuating lung injury. Patient self-inflicted lung injury (P-SILI) is a recently identified phenomenon that delves into the impact of spontaneous breathing on respiratory mechanics in patients with lung injury. While the studies are hypothesis-generating and have been demonstrated in animal and human studies, further clinical trials are needed to identify its impact on ARDS management. The purpose of this review article is to highlight the physiologic mechanisms of P-SILI, novel tools and methods to detect P-SILI, and to review the current literature on non-invasive and invasive respiratory management in patients with ARDS.
Keywords: acute hypoxic respiratory failure (AHRF); acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS); lung protective mechanical ventilation; patient self-inflicted lung injury (P-SILI).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bellani G., Laffey J.G., Pham T., Fan E., Brochard L., Esteban A., Gattinoni L., Van Haren F., Larsson A., McAuley D.F., et al. Epidemiology, Patterns of Care, and Mortality for Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 Countries. JAMA. 2016;315:788–800. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0291. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Roylance D. Stress-Strain Curves. Massachusetts Institute of Technology; Cambridge, UK: 2001.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources