Surface Chemistry of WC Powder Electrocatalysts Probed In Situ with NAP-XPS
- PMID: 40095698
- PMCID: PMC12184310
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202500965
Surface Chemistry of WC Powder Electrocatalysts Probed In Situ with NAP-XPS
Abstract
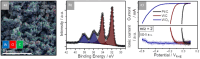
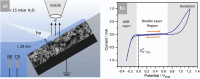
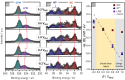
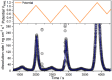
Tungsten carbide (WC) is a renowned compound catalyst material for electrochemical water splitting, and its high electrocatalytic activity toward the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) has been repeatedly reported. However, its susceptibility to oxidation raises the fundamental question of the underlying reason for its high activity, especially since passivation and thus potential deactivation can occur not only in air but also during reaction. Hence, the investigation of the surface chemistry under true operating conditions is crucial for a fundamental understanding of the electrocatalytic process. In this work, we use electrochemical X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (EC-XPS) to revisit the surface chemistry of WC powder electrodes in alkaline electrolyte in situ and under full potential control. Our results show that although the surface is initially covered with oxide, this passive film dissolves in the electrolyte under electrochemical reaction conditions. This clarifies the active surface termination during the HER and highlights the potential of laboratory-based EC-XPS to study applied energy conversion materials.
Keywords: Carbide; Electrocatalysis; Hydrogen evolution reaction; ICP‐MS; In situ XPS.
© 2025 The Author(s). Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nørskov J. K., Bligaard T., Rossmeisl J., Christensen C. H., Nat. Chem. 2009, 1, 37–46. - PubMed
-
- Michalsky R., Zhang Y.‐J., Medford A. J., Peterson A. A., J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 13026–13034.
-
- Kim S. K., Qiu Y., Zhang Y.‐J., Hurt R., Peterson A., Appl. Catal., B 2018, 235, 36–44.
-
- Hwu H. H., Chen J. G., Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 185–212. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

