Content-Based Histopathological Image Retrieval
- PMID: 40096145
- PMCID: PMC11902497
- DOI: 10.3390/s25051350
Content-Based Histopathological Image Retrieval
Abstract
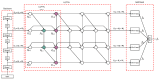
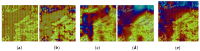
Feature descriptors in histopathological images are an important challenge for the implementation of Content-Based Image Retrieval (CBIR) systems, an essential tool to support pathologists. Deep learning models like Convolutional Neural Networks and Vision Transformers improve the extraction of these feature descriptors. These models typically generate embeddings by leveraging deeper single-scale linear layers or advanced pooling layers. However, these embeddings, by focusing on local spatial details at a single scale, miss out on the richer spatial context from earlier layers. This gap suggests the development of methods that incorporate multi-scale information to enhance the depth and utility of feature descriptors in histopathological image analysis. In this work, we propose the Local-Global Feature Fusion Embedding Model. This proposal is composed of three elements: (1) a pre-trained backbone for feature extraction from multi-scales, (2) a neck branch for local-global feature fusion, and (3) a Generalized Mean (GeM)-based pooling head for feature descriptors. Based on our experiments, the model's neck and head were trained on ImageNet-1k and PanNuke datasets employing the Sub-center ArcFace loss and compared with the state-of-the-art Kimia Path24C dataset for histopathological image retrieval, achieving a Recall@1 of 99.40% for test patches.
Keywords: content-based image retrieval; feature embedding; feature fusion; histopathological image; transfer learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Echoes of images: multi-loss network for image retrieval in vision transformers.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2024 Jul;62(7):2037-2058. doi: 10.1007/s11517-024-03055-6. Epub 2024 Mar 4. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2024. PMID: 38436836
-
BiU-net: A dual-branch structure based on two-stage fusion strategy for biomedical image segmentation.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2024 Jul;252:108235. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2024.108235. Epub 2024 May 18. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38776830
-
A novel biomedical image indexing and retrieval system via deep preference learning.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018 May;158:53-69. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.02.003. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018. PMID: 29544790
-
MESTrans: Multi-scale embedding spatial transformer for medical image segmentation.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2023 May;233:107493. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2023.107493. Epub 2023 Mar 17. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2023. PMID: 36965298
-
Multi-scale dual-channel feature embedding decoder for biomedical image segmentation.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2024 Dec;257:108464. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2024.108464. Epub 2024 Oct 18. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2024. PMID: 39447437
References
-
- Rahaman M.M., Li C., Wu X., Yao Y., Hu Z., Jiang T., Li X., Qi S. A Survey for Cervical Cytopathology Image Analysis Using Deep Learning. IEEE Access. 2020;8:61687–61710. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2983186. - DOI
-
- Solar M., Aguirre P. Deep learning techniques to process 3D chest CT. J. Univ. Comput. Sci. 2024;30:758. doi: 10.3897/jucs.112977. - DOI
-
- Hashimoto N., Takagi Y., Masuda H., Miyoshi H., Kohno K., Nagaishi M., Sato K., Takeuchi M., Furuta T., Kawamoto K., et al. Case-based similar image retrieval for weakly annotated large histopathological images of malignant lymphoma using deep metric learning. Med. Image Anal. 2023;85:102752. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2023.102752. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

