A supramolecular bactericidal material for preventing and treating plant-associated biofilms
- PMID: 40097425
- PMCID: PMC11914267
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-57839-x
A supramolecular bactericidal material for preventing and treating plant-associated biofilms
Abstract
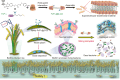
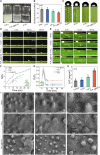
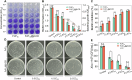
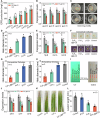
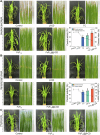
Treating bacterial biofilms on plants poses challenges due to biofilm induced resistance and poor agent adhesion on plant leaves. Here, we report on a host-guest self-assembled material which is biocompatible, has a lamellar supramolecular structure for leaf retention and prevents and treats bacterial biofilms. Phosphate/isopropanolamine-modified ferrocene forms a host-guest complex with β-CD which assembles into a lamella structure. The agent shows control efficacy against bacterial blight, bacterial leaf streak, and citrus canker in testing.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Fan, G. et al. Antimicrobial mechanisms of ZnO nanoparticles to phytopathogen Pseudomonas syringae: damage of cell envelope, suppression of metabolism, biofilm and motility, and stimulation of stomatal immunity on host plant. Pestic Biochem Phys194, 105455 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Ham, Y. & Kim, T. J. Anthranilamide from Streptomyces spp. inhibited Xanthomonas oryzae biofilm formation without affecting cell growth. Appl. Biol. Chem.61, 673 (2018).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

