CFD comparison of novel [emim][DCA] and [emim][MS] ionic liquids for the separation of CO2 greenhouse gas in the membrane contactor
- PMID: 40097466
- PMCID: PMC11914607
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-90289-5
CFD comparison of novel [emim][DCA] and [emim][MS] ionic liquids for the separation of CO2 greenhouse gas in the membrane contactor
Abstract
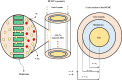
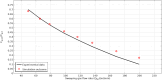
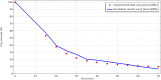
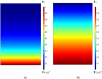
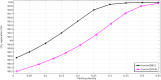
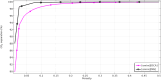
Global warming (resulted by the abnormal emission of CO2) has recently been an important global subject of concern due to its detrimental effects on the human well-being. Therefore, developing novel and cost-effective procedure for mitigating the CO2 release into the atmosphere is of prime importance. Recently, the employment of ionic liquids (ILs) for increasing the removal proficiency of CO2 in membrane-based processes has been a hot research topic among scientists. The emergence of indisputable positive points such as eco-friendliness, low flammability and negligible volatility have made the ILs a promising alternative for benchmark amine solutions. In this paper, the authors have made their effort to propose a numerical model following to a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation for estimating the separation percentage of CO2 pollutant using 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium dicyanamide ([emim][DCA]) and 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium methylsulfate ([emim][MS]) ILs in the hollow fiber membrane contactor (HFMC). Comparison of model outcomes with experimental-based results shows an appropriate agreement with absolute relative error (ARE) less than 5%.
Keywords: CO2 separation; Mathematical modeling; Membrane contactor; Novel ionic liquids; Simulation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Development of a CFD simulation for the analysis of CO2 separation percentage using novel [emim][C2N3] ionic liquid solution inside the gas-liquid contactor.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 21;15(1):2610. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-86468-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39837994 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical and Physical Ionic Liquids in CO2 Capture System Using Membrane Vacuum Regeneration.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Aug 15;12(8):785. doi: 10.3390/membranes12080785. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36005700 Free PMC article.
-
CO2 Desorption Performance from Imidazolium Ionic Liquids by Membrane Vacuum Regeneration Technology.Membranes (Basel). 2020 Sep 14;10(9):234. doi: 10.3390/membranes10090234. Membranes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32937879 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of ionic liquid-supported membranes for carbon dioxide capture: a review.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 May;29(24):35723-35745. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-19586-0. Epub 2022 Mar 8. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35260978 Review.
-
Tuning Functionalized Ionic Liquids for CO2 Capture.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 27;23(19):11401. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911401. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232702 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Imtiaz, A. et al. A critical review in recent progress of hollow fiber membrane contactors for efficient CO2 separations. Chemosphere 325, 138300 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Shiravi, A. et al. Hollow fiber Membrane Contactor for CO2 Capture: A Review of Recent Progress on Membrane Materials, Operational Challenges, scale-up and Economics10p. 100160 (Carbon Capture Science & Technology, 2024).
-
- Lee, H. J., Park, J. H. & Magnone, E. Study on design strategies and on new structure-performance relationships for CO2 capture in gas-liquid hollow fiber membrane contactors. J. Environ. Chem. Eng.12 (3), 112832 (2024).
-
- Marjani, A. et al. Mass transfer modeling absorption using nanofluids in porous polymeric membranes. J. Mol. Liq.318, 114115 (2020).
-
- Ahn, J. H. et al. Influence of various carbon capture technologies on the performance of natural gas-fired combined cycle power plants. J. Mech. Sci. Technol.33, 1431–1440 (2019).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

