MRI distortion correction is associated with improved local control in stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases
- PMID: 40097510
- PMCID: PMC11914157
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-93255-3
MRI distortion correction is associated with improved local control in stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases
Abstract
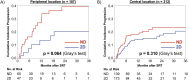
Distortions in brain MRI caused by gradient nonlinearities may reach several millimeters, thus distortion correction is strongly recommended for radiotherapy treatment planning. However, the significance of MRI distortion correction on actual clinical outcomes has not been described yet. Therefore, we investigated the impact of planning MRI distortion correction on subsequent local control in a historic series of 419 brain metastases in 189 patients treated with stereotactic radiotherapy between 01/2003 and 04/2015. Local control was evaluated using a volumetric extension of the RANO-BM criteria. The predictive significance of distortion correction was assessed using competing risk analysis. In this cohort, 2D distortion-corrected MRIs had been used for treatment planning in 52.5% (220/419) of lesions, while uncorrected MRIs had been employed in 47.5% (199/419) of metastases. 2D distortion correction was associated with improved local control (Cumulative incidence of local progression at 12 months: 14.3% vs. 21.2% and at 24 months: 18.7% vs. 28.6%, p = 0.038). In multivariate analysis, adjusting for histology, baseline tumor volume, interval between MRI and treatment delivery, year of planning MRI, biologically effective dose and adjuvant Whole-brain radiotherapy, use of distortion correction remained significantly associated with improved local control (HR 0.55, p = 0.020). This is the first study to clinically evaluate the impact of MRI gradient nonlinearity distortion correction on local control in stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases. In this historic series, we found significantly higher local control when using 2D corrected vs. uncorrected MRI studies for treatment planning. These results stress the importance of assuring that MR images used for radiotherapy treatment planning are properly distortion-corrected.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: Speaker fees from Siemens Healthineers (unrelated to this work): DH, MS, PS, FP. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Distortion inherent to magnetic resonance imaging can lead to geometric miss in radiosurgery planning.Pract Radiat Oncol. 2016 Nov-Dec;6(6):e319-e328. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2016.05.008. Epub 2016 Jun 1. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27523440 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating stereotactic accuracy with patient-specific MRI distortion corrections for frame-based radiosurgery.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Sep;25(9):e14472. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14472. Epub 2024 Jul 23. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 39042450 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging for brain stereotactic radiotherapy : A review of requirements and pitfalls.Strahlenther Onkol. 2020 May;196(5):444-456. doi: 10.1007/s00066-020-01604-0. Epub 2020 Mar 23. Strahlenther Onkol. 2020. PMID: 32206842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Geometric distortion assessment in 3T MR images used for treatment planning in cranial Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Radiotherapy.PLoS One. 2022 May 23;17(5):e0268925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268925. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35605005 Free PMC article.
-
LINAC based stereotactic radiosurgery for multiple brain metastases: guidance for clinical implementation.Acta Oncol. 2019 Sep;58(9):1275-1282. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2019.1633016. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Acta Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31257960 Review.
References
-
- Tabouret, E. et al. Recent trends in epidemiology of brain metastases: an overview. Anticancer Res.32(11), 4655–4662 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Gaudy-Marqueste, C. et al. Survival of melanoma patients treated with targeted therapy and immunotherapy after systematic upfront control of brain metastases by radiosurgery. Eur. J. Cancer84, 44–54 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Steinmann, D. et al. Quality of life in patients with limited (1–3) brain metastases undergoing stereotactic or whole brain radiotherapy: A prospective study of the DEGRO QoL working group. Strahlenther. Onkol.196(1), 48–57 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

