Overall survival with maintenance olaparib in platinum-sensitive relapsed ovarian cancer by somatic or germline BRCA and homologous recombination repair mutation status
- PMID: 40097725
- PMCID: PMC11997082
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-025-02966-x
Overall survival with maintenance olaparib in platinum-sensitive relapsed ovarian cancer by somatic or germline BRCA and homologous recombination repair mutation status
Abstract
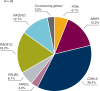
Background: The open-label, single-arm, multicentre ORZORA trial (NCT02476968) evaluated maintenance olaparib in patients with platinum-sensitive relapsed ovarian cancer (PSR OC) with a germline (g) or somatic (s) BRCA1 and/or BRCA2 mutation (BRCAm) or a non-BRCA homologous recombination repair mutation (non-BRCA HRRm).
Methods: Patients were in response to platinum-based chemotherapy after ≥2 prior lines of treatment and underwent prospective central screening for tumour BRCA status, then central gBRCAm testing to determine sBRCAm or gBRCAm status. An exploratory cohort evaluated non-BRCA HRRm in 13 predefined genes. Patients received olaparib 400 mg (capsules) twice daily until investigator-assessed disease progression. Secondary endpoints included overall survival (OS) and safety.
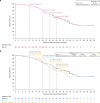
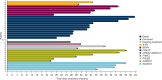
Results: 177 patients received olaparib. At the final data cutoff (25 June 2021), median OS from study enrolment was 46.8 (95% confidence interval [CI] 37.9-54.4), 43.2 (31.7-NC [not calculated]), 47.4 (37.9-NC) and 44.9 (28.9-NC) months in the BRCAm, sBRCAm, gBRCAm and non-BRCA HRRm cohorts, respectively. No new safety signals were identified.
Conclusion: Maintenance olaparib showed consistent clinical activity in the BRCAm and sBRCAm cohorts; exploratory analysis suggested similar activity in the non-BRCA HRRm cohort. These findings highlight that patients with PSR OC, beyond those with gBRCAm, may benefit from maintenance olaparib.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate: The trial was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, Good Clinical Practice Guidelines and the AstraZeneca policy of bioethics ( https://www.astrazeneca.com/content/dam/az/PDF/2019/Bioethics%20Policy%20final.pdf ) was approved by the Ethics Committee of Istituto Nazionale Tumori ‘Fondazione G Pascale’ (Reference no. 25/15). All patients provided written informed consent. Competing interests: Sandro Pignata: Honoraria from AstraZeneca, Merck Sharp & Dohme (MSD), Roche, Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) and Clovis Pharma; and research funding from Roche, MSD, AstraZeneca and Pfizer. Amit Oza: Principal investigator of investigator-initiated studies with AstraZeneca; institutional grant funding from AstraZeneca; and steering committee member (non-compensated) for AstraZeneca, Clovis Oncology and GSK. Geoff Hall: Research funding from IQVIA. Beatriz Pardo: Research funding from AstraZeneca, GSK, Clovis and MSD. Radoslaw Madry: Advisory board participation for AstraZeneca, Roche and GSK; and personal fees from AstraZeneca, Roche and GSK. David Cibula: Advisory board participation for AstraZeneca, Roche, Genmab, SOTIO, Merck and GSK. Jaroslav Klat: Reports no disclosures. Ana Montes: Reports no disclosures. Rosalind Glasspool: Principal investigator for trials sponsored by AstraZeneca, Clovis, Tesaro, Immunogen, Pfizer and Lilly; research funding from Clovis, Boehringer Ingelheim and Lilly/Ignyta; institution research funding from Tesaro; institutional fees from Novartis; and personal fees from AstraZeneca, MSD, Clovis, Tesaro, GSK, Immunogen and SOTIO. Nicoletta Colombo: Personal fees from AstraZeneca, MSD, Roche, Tesaro, GSK, Clovis Oncology, PharmaMar, Pfizer, Amgen, Novartis, BIODCAD and Immunogen. Imre Pete: Reports no disclosures. Ana Herrero Ibáñez: Consulting/advisory board participation for GSK; speakers’ bureau participation for Clovis, GSK, MSD, PharmaMar; and research funding from AstraZeneca and Roche. Margarita Romeo: Institution research funding from AstraZeneca, GSK, Clovis and Pfizer; personal fees from MSD and GSK; and AstraZeneca employment (this author became an AstraZeneca employee in July 2024; her contributions to this manuscript were made while working at her previous institution). Rumyana Ilieva: Reports no disclosures. Constanta Timcheva: Principal investigator of clinical trials of AstraZeneca, Roche, Novartis, Pfizer and Merck; and member of advisory boards of Astellas, Servier and Novartis. Massimo Di Maio: Principal investigator of clinical trials of Roche, Merck, BeiGene, Novartis, Pfizer and Exelixis; member of advisory boards of AstraZeneca, Roche, Novartis, Pfizer, Eisai, Astellas, Janssen, Merck and Amgen; and institutional research funding from GSK/Tesaro. Zahid Bashir: AstraZeneca employment (at time of study); and stock ownership of Omniac Pharm Consult Ltd. Rosie Taylor: AstraZeneca employment and stock ownership. Alan Barnicle: AstraZeneca employment and stock ownership. Andrew Clamp: Research funding from AstraZeneca; and honoraria from AstraZeneca, Clovis Oncology, GSK/Tesaro and Eisai.
Figures
References
-
- AstraZeneca. Lynparza receives approval in Japan for the treatment of advanced ovarian cancer. 2018. https://www.astrazeneca.com/media-centre/press-releases/2018/lynparza-re.... Accessed 25 February 2025.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

