The Effects of Metabolic Bariatric Surgery on Intra-pancreatic Fat Deposition and Total Pancreas Volume: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 40097776
- PMCID: PMC11976765
- DOI: 10.1007/s11695-025-07778-9
The Effects of Metabolic Bariatric Surgery on Intra-pancreatic Fat Deposition and Total Pancreas Volume: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
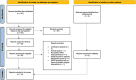
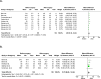
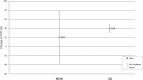
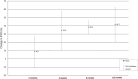
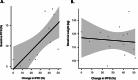
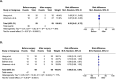
Bariatric procedures are common interventions for weight loss and metabolic improvements; yet, their effects on the pancreas-a key metabolic organ-are largely unknown. This systematic review aimed to summarise data on changes in intra-pancreatic fat deposition (IPFD) and total pancreas volume (TPV) following metabolic bariatric surgery and endoscopic bariatric therapy. The literature search was conducted in MEDLINE and Embase databases. Studies in humans were included if they reported on changes in IPFD and/or TPV from before to after bariatric procedure. Random effects meta-analysis was conducted. Fourteen studies (all involving metabolic bariatric surgery) met the eligibility criteria. Metabolic bariatric surgery resulted in a mean absolute IPFD reduction of 3.9% (p = 0.003) and a mean TPV decrease of 10.7 cm3 (p < 0.001). The mean relative IPFD reduction after metabolic bariatric surgery was 35.9%. Sleeve gastrectomy led to a higher mean relative IPFD reduction than Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (39.9% vs. 20.6%), though this difference was not statistically significant. Analysis of follow-up duration showed a mean relative IPFD reduction of 8.8% in patients with follow-ups of less than 3 months. Metabolic bariatric surgery leads to significant reductions in IPFD and TPV. Follow-up should take place no earlier than 3 months for the full benefits of bariatric procedures on the pancreas to manifest.
Keywords: Endoscopic bariatric therapy; Fatty pancreas disease; Intra-pancreatic fat deposition; Metabolic bariatric surgery; Total pancreas volume.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Artificial intelligence-based models for quantification of intra-pancreatic fat deposition and their clinical relevance: a systematic review of imaging studies.Eur Radiol. 2025 Jul 19. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11808-6. Online ahead of print. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40682667 Review.
-
Surgery for weight loss in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Aug 8;2014(8):CD003641. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003641.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25105982 Free PMC article.
-
Prepregnancy Roux-en-Y gastric bypass vs sleeve gastrectomy: a systematic review, pairwise, and network meta-analysis of obstetrical and neonatal outcomes.Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2023 Jun;5(6):100914. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2023.100914. Epub 2023 Mar 7. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2023. PMID: 36889438
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of bariatric (weight loss) surgery for obesity: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2009 Sep;13(41):1-190, 215-357, iii-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta13410. Health Technol Assess. 2009. PMID: 19726018
-
Position statement and guidelines about Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG) also known as "Endo-sleeve".J Visc Surg. 2025 Feb;162(1):71-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jviscsurg.2024.12.003. Epub 2025 Jan 9. J Visc Surg. 2025. PMID: 39794164 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship of Fat Deposition in the Liver and Pancreas with Cholecystectomy.Obes Facts. 2025 Apr 10:1-13. doi: 10.1159/000545781. Online ahead of print. Obes Facts. 2025. PMID: 40209687 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity and Pancreatic Diseases: From Inflammation to Oncogenesis and the Impact of Weight Loss Interventions.Nutrients. 2025 Jul 14;17(14):2310. doi: 10.3390/nu17142310. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40732935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial intelligence-based models for quantification of intra-pancreatic fat deposition and their clinical relevance: a systematic review of imaging studies.Eur Radiol. 2025 Jul 19. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11808-6. Online ahead of print. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40682667 Review.
References
-
- Lazzati A. Epidemiology of the surgical management of obesity. J Visc Surg. 2023;160(2S):S3–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

