New insights on anti-tumor immunity of CD8+ T cells: cancer stem cells, tumor immune microenvironment and immunotherapy
- PMID: 40097979
- PMCID: PMC11912710
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-025-06291-y
New insights on anti-tumor immunity of CD8+ T cells: cancer stem cells, tumor immune microenvironment and immunotherapy
Abstract
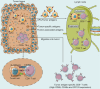
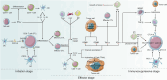
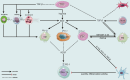
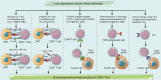
Recent breakthroughs in tumor immunotherapy have confirmed the capacity of the immune system to fight several cancers. The effective means of treating cancer involves accelerating the death of tumor cells and improving patient immunity. Dynamic changes in the tumor immune microenvironment alter the actual effects of anti-tumor drug production and may trigger favorable or unfavorable immune responses by modulating tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Notably, CD8+ T cells are one of the primary tumor-infiltrating immune cells that provide anti-tumor response. Tumor cells and tumor stem cells will resist or evade destruction through various mechanisms as CD8+ T cells exert their anti-tumor function. This paper reviews the research on the regulation of tumor development and prognosis by cancer stem cells that directly or indirectly alter the role of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells. We also discuss related immunotherapy strategies.
Keywords: Cancer prognosis; Cancer stem cell (CSC); Cytotoxic CD8+ T lymphocyte (CTL); Immunotherapy; Tumor immune microenvironment (TIME).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

