Clozapine-induced obsessive-compulsive symptoms in schizophrenia: Clinical and cognitive determinants of dysfunctional checking
- PMID: 40098472
- PMCID: PMC12080643
- DOI: 10.1017/S0033291724003350
Clozapine-induced obsessive-compulsive symptoms in schizophrenia: Clinical and cognitive determinants of dysfunctional checking
Abstract
Background: Obsessive-compulsive symptoms (OCS) emerge in a significant proportion of clozapine-treated schizophrenia patients, affecting social functioning and increasing depressive symptoms. This study investigates the underexplored cognitive mechanisms of clozapine-induced OCS, particularly focusing on dysfunctional checking behavior.
Methods: Clinical and cognitive profiles of OCS and their relationship to dysfunctional checking were investigated using a novel checking paradigm (image verification task or IVT) in four groups: clozapine-treated schizophrenia patients with clozapine-induced OCS (SCZ-OCS, n = 21) and without (SCZ-only, n = 15), patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD, n = 32) and IQ-matched healthy volunteers (HV, n = 30).
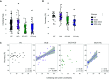
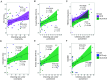
Results: Only SCZ-OCS patients showed a distinctive pattern of dysfunctional checking on the IVT. Compared with SCZ-OCS, SCZ-only patients exhibited functional checking while having equivalent deficits in executive cognition, clozapine dose, and treatment duration, though with less severe positive and depressive symptoms. In SCZ-OCS, dysfunctional checking was positively correlated with clozapine dose and working memory performance. By contrast, OCD patients' checking was positively related to intolerance of uncertainty. Checking in the OCD and SCZ-OCS groups was positively correlated with YBOCS-compulsion.
Conclusion: This study is the first to compare the distinct cognitive and clinical profiles of SCZ-OCS, SCZ-only, and OCD, with a focus on checking behavior, a major symptom in clozapine-treated patients. We introduced a novel and sensitive measure for checking, which showed dysfunctional checking only in SCZ-OCS patients treated with clozapine. These findings indicate that a subset of patients with schizophrenia with more severe positive symptoms and cognitive deficits are especially susceptible to OCD symptoms when treated with clozapine.
Keywords: OCD; checking; cognitive flexibility; schizophrenia; spatial working memory.
Figures

References
-
- Bıçakcı Ay, Ş., Oğuz, K. K., Özçelik Eroğlu, E., Has, A. C., & Ertuğrul, A. (2023). A diffusion tensor imaging study in schizophrenia patients with clozapine induced obsessive compulsive symptoms. Human Psychopharmacology: Clinical and Experimental, 38(1), Article e2857. 10.1002/hup.2857 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Biria, M., Banca, P., Keser, E., Healy, M. P., Sawiak, S. J., Marzuki, A. A., … & Robbins, T. W. (2024). Excessive Checking in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: Neurochemical Correlates Revealed by 7T Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Biological Psychiatry Global Open Science, 4(1), 363–373. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

