Loss of CYLD promotes splenic marginal zone lymphoma
- PMID: 40098895
- PMCID: PMC11911931
- DOI: 10.1002/hem3.70098
Loss of CYLD promotes splenic marginal zone lymphoma
Abstract
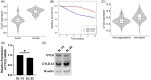
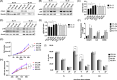
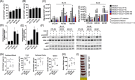
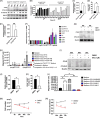
Splenic marginal zone lymphoma (SMZL) is a distinct clinical and pathological entity among marginal zone lymphomas. Genetic and microenvironmental factors leading to aberrant activation of the NF-κB pathway have been implicated in SMZL pathogenesis. CYLD is a negative regulator of NF-κB and other signaling pathways acting as a deubiquitinase of regulatory molecules and has been reported as a tumor suppressor in different types of cancer, including B-cell malignancies. To assess whether CYLD is implicated in the natural history of SMZL, we profiled primary cells from patients with SMZL and SMZL cell lines for CYLD expression and functionality. We report that CYLD is downregulated in patients with SMZL and that CYLD ablation in vitro leads to NF-κB pathway hyperactivation, promoting the proliferation of SMZL cells. In addition, we found that CYLD deficiency was associated with increased migration of SMZL cells in vitro, through CCR7 receptor signaling, and with increased dissemination in vivo. CYLD loss was sufficient to induce BcR signaling, conferring increased resistance to ibrutinib treatment in vitro. In summary, our work uncovers a novel role of CYLD as a key regulator in SMZL pathogenesis, dissemination, and resistance to targeted agents. On these grounds, CYLD could be proposed as a novel target for patient stratification and personalized interventions.
© 2025 The Author(s). HemaSphere published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Hematology Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Paolo Ghia: honoraria/advisory board: AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, BMS, Galapagos, Janssen, Loxo/Lilly, MSD, Roche; research funding: AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BMS, Janssen; Kostas Stamatopoulos: honoraria/advisory board: AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Gilead, Janssen; research funding: AbbVie, Gilead, Janssen; José Ángel Martínez Climent: research funding: AstraZeneca, BMS‐Celgene, Janssen, Palleon, Roche‐Genentech; Davide Rossi: honoraria/research funding: AbbVie, AstraZeneca; Cellestia, Gilead, Janssen, Verastem, Roche; Lydia Scarfò: advisory board: AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Janssen.
Figures
References
-
- Armitage JO, Weisenburger DD. New approach to classifying non‐Hodgkin's lymphomas: clinical features of the major histologic subtypes. Non‐Hodgkin's Lymphoma Classification Project. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16(8):2780‐2795. - PubMed
-
- Martínez N, Almaraz C, Vaqué JP, et al. Whole‐exome sequencing in splenic marginal zone lymphoma reveals mutations in genes involved in marginal zone differentiation. Leukemia. 2014;28(6):1334‐1340. - PubMed
-
- Clipson A, Wang M, de Leval L, et al. KLF2 mutation is the most frequent somatic change in splenic marginal zone lymphoma and identifies a subset with distinct genotype. Leukemia. 2015;29(5):1177‐1185. - PubMed
-
- Bikos V, Darzentas N, Hadzidimitriou A, et al. Over 30% of patients with splenic marginal zone lymphoma express the same immunoglobulin heavy variable gene: Ontogenetic implications. Leukemia. 2012;26(7):1638‐1646. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
