The effect of exposure to the COVID-19 pandemic on nutritional status and cognitive, motor, and behavioural development among children aged 20 months in rural Bangladesh: A repeated cross-section study between 2020 and 2022
- PMID: 40100815
- PMCID: PMC11918444
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309836
The effect of exposure to the COVID-19 pandemic on nutritional status and cognitive, motor, and behavioural development among children aged 20 months in rural Bangladesh: A repeated cross-section study between 2020 and 2022
Abstract
Background: Past studies have documented detrimental effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the learning and mental health of preschool- and school-age children. Few studies have examined effects on younger children's development, though this age group is extremely sensitive to economic and health shocks.
Methods: We assessed the effects of exposure to the pandemic on the cognitive, language, and motor development; behaviour; and growth among toddlers in rural Bangladesh. We estimated average differences between two repeated cross-sectional surveys of children and mothers living in the same villages. The first survey included 20-month-old children in 2019 and 2020 (unexposed group). The second survey took place in a randomly-selected subset of the same villages in 2022 among 20-month-old children, who had experienced pandemic-related lockdowns from approximately mid-gestation through their first year (exposed group). Both surveys used similar inclusion criteria and the same developmental assessments (Bayley's Scales of Infant and Toddler Development), behaviour observations, and field protocols.
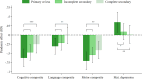
Results: The exposed group (N = 526) had lower cognitive [Effect size = -0.45 (95% CI = -0.63 to -0.27)] and motor [-0.55 (-0.73 to -0.37)] composite scores, compared to the unexposed group (N = 1344). They were also observed to be less responsive to the examiner [-0.29 (-0.48 to -0.11)], less happy [-0.37 (-0.55 to -0.19)], less vocal [-0.57 (-0.73 to -0.4)] and less cooperative [-0.42 (-0.6 to -0.24)]. The pandemic increased depression among mothers with a primary education or less but not among better educated mothers. Children of less educated mothers also showed larger differences across exposed and unexposed groups in development and behaviour than those with better educated mothers.
Conclusion: The COVID-19 pandemic detrimentally affected cognitive and motor skills and behaviour of young children in rural Bangladesh. Disadvantaged young children's development appears to be extremely vulnerable to shocks. Without intervention these deficits will likely lead to later problems in learning and mental health.
Copyright: © 2025 Hamadani et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Schady N, Holla A, Sabarwal S, Silva J. Collapse and Recovery: How the COVID-19 Pandemic Eroded Human Capital and What to Do about It: World Bank Publications; 2023.
-
- Abufhele A, Bravo D, López Bóo F, Soto-Ramirez P. Developmental losses in young children from pre-primary program closures during the COVID-19 pandemic. IZA Discussion Paper No. 15179 2022.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

