A comprehensive and standardized pipeline for automated profiling of higher cognition in mice
- PMID: 40101715
- PMCID: PMC12049718
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2025.101011
A comprehensive and standardized pipeline for automated profiling of higher cognition in mice
Abstract
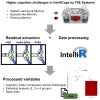
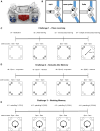
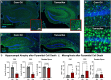
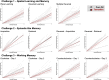
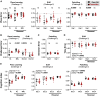
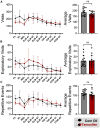
In rodent behavior research, observer-independent methods, such as the IntelliCage, enhance data collection in a social, and thus stress-reduced, environment. The IntelliCage system allows experimenters to create cognitive challenges for mice motivated by rewards. Given the extensive and diverse data from IntelliCage, there is a high demand for automated analysis. Here, we introduce IntelliR, a free and standardized pipeline for analyzing IntelliCage data, including a cognition index for performance comparison across challenges. IntelliR supports the automatic analysis of three challenges that cover spatial, episodic-like, and working memory with their reversal tests and can also be adapted for other designs. Results from three cohorts of adult female C57B6 mice showed improved task proficiency over time. To validate cognitive impairment detection, we used adult female NexCreERT2xRosa26-eGFP-DTA mice after neuron ablation in cortex and hippocampus, in which we observed reduced learning capabilities. IntelliR integrates easily into research, improving time management and reproducibility.
Keywords: CP: neuroscience; IntelliCage; automated phenotyping; behavior; cognitive domains; cognitive flexibility; episodic-like memory; reversal learning; spatial memory; working memory.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Dere E., Dahm L., Lu D., Hammerschmidt K., Ju A., Tantra M., Kästner A., Chowdhury K., Ehrenreich H. Heterozygous ambra1 deficiency in mice: a genetic trait with autism-like behavior restricted to the female gender. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2014;8:181. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00181. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- El-Kordi A., Winkler D., Hammerschmidt K., Kästner A., Krueger D., Ronnenberg A., Ritter C., Jatho J., Radyushkin K., Bourgeron T., et al. Development of an autism severity score for mice using Nlgn4 null mutants as a construct-valid model of heritable monogenic autism. Behav. Brain Res. 2013;251:41–49. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2012.11.016. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Galsworthy M.J., Amrein I., Kuptsov P.A., Poletaeva I.I., Zinn P., Rau A., Vyssotski A., Lipp H.P. A comparison of wild-caught wood mice and bank voles in the Intellicage: assessing exploration, daily activity patterns and place learning paradigms. Behav. Brain Res. 2005;157:211–217. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2004.06.021. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

