Nivolumab adjuvant to chemo-radiation in localized muscle-invasive urothelial cancer: primary analysis of a multicenter, single-arm, phase II, investigator-initiated trial (NEXT)
- PMID: 40102029
- PMCID: PMC11927433
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2024-010572
Nivolumab adjuvant to chemo-radiation in localized muscle-invasive urothelial cancer: primary analysis of a multicenter, single-arm, phase II, investigator-initiated trial (NEXT)
Abstract
Background: Muscle-invasive urothelial cancer (UC) has a high risk of recurrence after definitive treatment. Nivolumab adjuvant to radical surgery improves disease-free survival in patients with UC with a high risk of recurrence; however, its role adjuvant to chemoradiation therapy (CRT) is unknown.
Methods: The NEXT trial is a single-arm, phase-2 study evaluating the efficacy and tolerability of nivolumab adjuvant to CRT in patients with localized or locoregional UC. The primary endpoint is failure-free survival (FFS) at 2 years. Secondary endpoints include patterns of recurrence, toxicity and quality of life (QoL). Plasma cell-free DNA (cfDNA) was subjected to shallow whole-genome sequencing to correlate with outcomes.
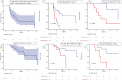
Results: 28 patients were enrolled and received 480 mg of nivolumab intravenously every 4 weeks for up to 12 cycles adjuvant to CRT. The FFS at 2 years was 33.2% (95% CI 18.5% to 59.6%). Nine (32%) patients had localized progression, and eight (29%) had distant progression. 25 (89%) had one or more high-risk features (ie, plasmacytoid differentiation, T4, N+, multiple tumors, tumors >5 cm, residual disease before CRT, carcinoma in situ, and hydronephrosis). Patients with ≤2 high-risk features had a median FFS of 45.2 months (95% CI 14.56 to not reached (NR)) compared with 8.2 months (95% CI 7.1 to NR) in those with three or more risk features (p=0.0024). Nivolumab-associated treatment-related adverse events occurred in 18 (64.3%) patients, only 3 had grade 3 TRAEs, with significant changes in QoL. Plasma cfDNA copy number instability (CNI) scores ≤25 before the first dose of adjuvant nivolumab and at cycle 4 were associated with better overall survival compared with CNI scores ≥26 (49.6 months vs 20.5 months, p=0.0024). Genome copy number changes indicated chromatin remodeling and tyrosine kinase pathways, among others, as oncogenic drivers implicated in progression.
Conclusion: Nivolumab adjuvant to CRT in localized or locally advanced UC is well tolerated. Stratification by risk factors and correlation with plasma cfDNA analyses generate hypotheses for potential patient selection and putative therapeutic targets for future study.
Trial registration number: NCT03171025.
Keywords: Bladder Cancer; Circulating tumor DNA - ctDNA; Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: DG reports consultancy to MyCarGorithm. BLM reports consultancy to Astellas, AVEO, Bavarian Nordig, Bayer, Bristo-Myers Squibb, Clovis Oncology, Exelixis, Janssen Oncology, Merck, Peloton Therapeutics, Pfizer and Tempus; and research funding from Bavarian Nordic, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Clovis Oncology. RKJ reports consulting to AVEO, Bristo-Myers Squibb, EMD Serono and Gilead Sciences; and research funding to Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences and the NCI. JB reports being employed by Chronix Biomedical and Oncocyte. ES reports being employed by OncoCyte. RL reports consultancy to Arquer iagnostics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CG Oncology, FerGene, Ferring, Lucence Diagnostics, Merck and Urogen pharma; and Research funding from G Oncology, and Predicine. SL reports consultancy to Cancer Study Group. JT reports consultancy to Bayer, Blue Earth Diagnostics, Boston Scientific, Boston Scientific, Janssen Scientific Affairs, Lantheus Medical Imaging, Merck, Myovant Sciences, Myriad Genetics, Myriad Genetics, and Myriad Genetics; and Research funding from Bayer (Inst), and Myriad Genetics (Inst). US reports consultancy to Astellas, AstraZeneca, Adaptimmune, Exelixis, Gilead, Imvax, Pfizer, Seattle Genetics and Sanofi and research funding from institute from Janssen, Exelixis and Astellas/Seattle Genetics. NA reports research funding from Amgen (Inst), Arvinas (Inst), AstraZeneca (Inst), Bayer (Inst), Bristol-Myers Squibb (Inst), Calithera Biosciences (Inst), Celldex (Inst), crispr therapeutics (Inst), Eisai (Inst), Exelixis (Inst), Genentech (Inst), Gilead Sciences (Inst), Immunomedics (Inst), Janssen (Inst), Lilly (Inst), Merck (Inst), Nektar (Inst), ORIC Pharmaceuticals (Inst), ORIC Pharmaceuticals (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), and Takeda (Inst). SG reports research funding from Acrotech Biopharma (Inst), AstraZeneca (Inst), Bristol-Myers Squibb (Inst), Clovis Oncology (Inst), Daiichi Sankyo/Lilly (Inst), Five Prime Therapeutics (Inst), Hoosier Cancer Research Network (Inst), Immunocore (Inst), Incyte (Inst), LSK BioPharma (Inst), MedImmune (Inst), Merck (Inst), Mirati Therapeutics (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), QED Therapeutics (Inst), Rexahn Pharmaceuticals (Inst), Seagen (Inst), and Viralytics (Inst). All other authors have no pertinent interests to report.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
