Testicular ultrasound: an emergency medicine perspective
- PMID: 40102331
- PMCID: PMC12130081
- DOI: 10.1007/s11739-025-03864-z
Testicular ultrasound: an emergency medicine perspective
Abstract
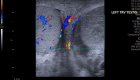
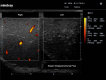
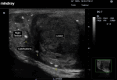
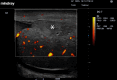
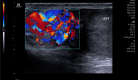
Ultrasound of the scrotum plays a crucial role in assessing acute scrotal conditions in the Emergency Department. Although the Emergency Physician and Intensivist have shared responsibility for the care of the critically ill patient, the Emergency Physician typically uses Point-of-care Ultrasound in a broader range of applications than the intensivist to include advanced abdominal, obstetric, testicular, musculoskeletal, and ocular ultrasonography. Acute scrotum refers to the sudden onset of scrotal erythema, swelling, or pain, and it is not a rare condition in the Emergency Department. Prompt intervention is required in cases of testicular torsion or rupture, and ultrasound of the scrotum has high utility for emergency physicians seeing acute scrotal complaints with any frequency. However, the incidence of acute scrotum incidence is low compared to other disease states requiring ultrasound diagnosis. This presents a problem when considering ultrasound training of Emergency Physicians for ultrasound of the scrotum in a Point-of-care perspective. With this narrative review, we will attempt to raise the awareness of emergency medicine doctors to the importance of ultrasound of the scrotum in the Emergency Department. We will also discuss educational aspects in testicular ultrasound and the use of contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Finally, we propose an algorithm for action.
Keywords: Acute scrotum; Doppler; Testis; Torsion.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflicts of interest: Not applicable. Ethical approval: Not applicable. Informed consent: For this type of study, informed consent was not required.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Accuracy of point-of-care ultrasound by pediatric emergency physicians for testicular torsion.J Pediatr Urol. 2019 Dec;15(6):608.e1-608.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2019.07.003. Epub 2019 Jul 12. J Pediatr Urol. 2019. PMID: 31455581
-
Testicular ultrasound.Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2004 Aug;22(3):723-48, ix. doi: 10.1016/j.emc.2004.04.002. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2004. PMID: 15301848 Review.
-
Emergency ultrasound of acute scrotal pain.Eur J Emerg Med. 2015 Feb;22(1):2-9. doi: 10.1097/MEJ.0000000000000123. Eur J Emerg Med. 2015. PMID: 24910960 Review.
-
Emergency ultrasonography in the evaluation of the acute scrotum.Acad Emerg Med. 2001 Jan;8(1):85-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2001.tb00562.x. Acad Emerg Med. 2001. PMID: 11136158
-
Detection of Testicular Torsion With Preserved Intratesticular Flow By Point of Care Ultrasound in the Emergency Department: A Case Report.J Emerg Med. 2022 Apr;62(4):e88-e90. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2021.11.018. Epub 2022 Jan 22. J Emerg Med. 2022. PMID: 35078703
References
-
- Mariz J (2018) Ecografia à Cabeceira do Doente na Medicina Interna: Uma Mudança de Paradigma na Avaliação do Doente Agudo. Med Interna (Bucur) 19:25
-
- Blaivas M, Brannam L (2004) Testicular ultrasound. Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America, vol 22. WB Saunders, US, pp 723–48 - PubMed
-
- Yagil Y, Naroditsky I, Milhem J, Leiba R, Leiderman M, Badaan S et al (2010) Role of Doppler Ultrasonography in the Triage of Acute Scrotum in the Emergency Department. J Ultrasound Med. 29(1):11–21. 10.7863/jum.2010.29.1.11 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

