Guanine nucleotide biosynthesis blockade impairs MLL complex formation and sensitizes leukemias to menin inhibition
- PMID: 40102405
- PMCID: PMC11920272
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-57544-9
Guanine nucleotide biosynthesis blockade impairs MLL complex formation and sensitizes leukemias to menin inhibition
Abstract
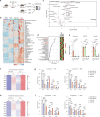
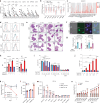
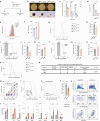
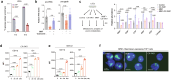
Targeting the dependency of MLL-rearranged (MLLr) leukemias on menin with small molecule inhibitors has opened new therapeutic strategies for these poor-prognosis diseases. However, the rapid development of menin inhibitor resistance calls for combinatory strategies to improve responses and prevent resistance. Here we show that leukemia stem cells (LSCs) of MLLr acute myeloid leukemia (AML) exhibit enhanced guanine nucleotide biosynthesis, the inhibition of which leads to myeloid differentiation and sensitization to menin inhibitors. Mechanistically, targeting inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase 2 (IMPDH2) reduces guanine nucleotides and rRNA transcription, leading to reduced protein expression of LEDGF and menin. Consequently, the formation and chromatin binding of the MLL-fusion complex is impaired, reducing the expression of MLL target genes. Inhibition of guanine nucleotide biosynthesis or rRNA transcription further suppresses MLLr AML when combined with a menin inhibitor. Our findings underscore the requirement of guanine nucleotide biosynthesis in maintaining the function of the LEDGF/menin/MLL-fusion complex and provide a rationale to target guanine nucleotide biosynthesis to sensitize MLLr leukemias to menin inhibitors.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: K.T. received consultancy fees from Symbio Pharmaceuticals, honoraria from Mission Bio, Otsuka, and Illumina, and research funding from Onconova, ASTEX, and Jazz pharmaceuticals. G.C.I. received consultancy or advisory role fees from Novartis, Kura Oncology, Syndax Pharmaceuticals, Abbvie, Sanofi and NuProbe and received research funding from Celgene, Novartis, Kura Oncology, Syndax Pharmaceuticals, Merck, Cullinan Oncology, Astex, NuProbe, and received research funding from Break Through Cancer. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA260729/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01CA265748/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01CA237291/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01 CA193235/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50CA100632/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01HL165145/National Heart and Lung Institute (NHLI)
- R01 HL165145/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA255813/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01 CA264932/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA260729/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01CA193235/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01 CA255813/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA264932/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

