Synthesis, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and cytotoxicity of new pyrimidine and pyrimidopyrimidine derivatives
- PMID: 40102434
- PMCID: PMC11920053
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-92066-w
Synthesis, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and cytotoxicity of new pyrimidine and pyrimidopyrimidine derivatives
Abstract
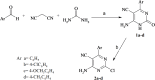
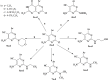
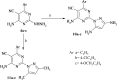
A series of novel pyrimidine and pyrimidopyrimidine analogs were synthesized in good yield from 6-amino-4-aryl-2-oxo-pyrimidine-5-carbonitrile (1a-d). The synthesized compounds were characterized using various spectral studies, including FT-IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, mass spectrometry, and elemental analysis. Newly synthesized pyrimidopyrimidines and 2-(substituted-pyrazolyl)pyrimidine derivatives were assessed in vitro for their cytotoxic activities against three cancerous cell lines: colorectal carcinoma (HCT-116), mammary gland breast cancer (MCF-7), and hepatocellular carcinoma (HEPG-2), as well as normal fibroblasts (W138). The results indicated that compounds 3b, 10b, and 10c exhibited the highest cytotoxic activities, with IC50 values very close to those of the reference drug (doxorubicin) across all studied cancerous cell lines, while also demonstrating good safety effects on the normal human lung fibroblast cell line. Furthermore, all the synthesized compounds were examined for their antimicrobial activity against two Gram-positive bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis), one Gram negative bacterium (Escherichia coli) and two fungal species (Candida albicans and Aspergillus flavus). The antimicrobial results of the synthesized compounds, when compared with the reference drugs ampicillin and clotrimazole, revealed that compounds 3a, 3b, 3d, 4a-d, 9c and 10b exhibited excellent antimicrobial activities. Moreover, membrane stabilization or anti-hemolytic activity was employed as a method to study the in vitro anti-inflammatory activity of the prepared heterocyclic compounds. Antioxidant activities were also assessed by measuring the percentage of free radical scavenging. Compounds 4b, 10c and 11a-c demonstrated strong anti-hemolytic and antioxidant effects, which can be attributed to their ability to protect red blood cells from hemolysis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis, molecular docking and in silico ADMET profile of pyrano[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives as antimicrobial and anticancer agents.Bioorg Chem. 2021 Oct;115:105186. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105186. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 34314914
-
Green, facile synthesis and evaluation of unsymmetrical carbamide derivatives as antimicrobial and anticancer agents with mechanistic insights.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 4;14(1):15441. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65308-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38965246 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of certain pyrimidine derivatives as antimicrobial agents and anti-inflammatory agents.Molecules. 2010 Mar 15;15(3):1882-90. doi: 10.3390/molecules15031882. Molecules. 2010. PMID: 20336018 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, Characterization, Antimicrobial Activity and Anticancer of Some New Pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines and Pyrazolo[5,1-c]1,2,4-triazines.Med Chem. 2020;16(6):750-760. doi: 10.2174/1573406415666190620144404. Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31218963
-
Application of microbial pigments in the pharmaceutical industry: current status and opportunities.Arch Microbiol. 2025 Mar 31;207(5):104. doi: 10.1007/s00203-025-04261-y. Arch Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40164794 Review.
Cited by
-
Sustainable synthesis of Schiff base derivatives via an ionic liquid and a microwave-assisted approach: structural, biological, and computational evaluation.RSC Adv. 2025 Jul 3;15(28):22764-22788. doi: 10.1039/d5ra02622a. eCollection 2025 Jun 30. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40612636 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ajmal, R. B. Biological activity of pyrimidine derivatives: a review. Org. Med. Chem. Int. J.2 (2), 55581 (2017).
-
- Jain, K. S. et al. Biological and medicinal significance of pyrimidines. Curr. Sci.90 (6), 793–803 (2006).
-
- Madadi, N. R., Penthala, N. R., Janganati, V. & Crooks, P. A. Synthesis andantiproliferative activity of aromatic substituted 5-((1-benzyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methylene)-1,3-dimethyl pyrimidine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione analogs against human tumor cell lines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.24, 601–603 (2014). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu, K. et al. Multisubstituted quinoxalines and pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidines: synthesis and SAR study as tyrosine kinase c-Met inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.22, 6368–6372 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Jiao, X. Y. et al. Synthesis and optimization of substituted furo[2,3-d]-pyrimidin-4-amines and 7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-amines as ACK1 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.22, 6212–6217 (2012). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

