Life's Crucial 9 and NAFLD from association to SHAP-interpreted machine learning predictions
- PMID: 40102489
- PMCID: PMC11920226
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-92777-0
Life's Crucial 9 and NAFLD from association to SHAP-interpreted machine learning predictions
Abstract
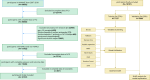
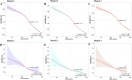
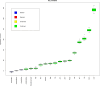
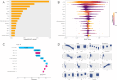
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most prevalent chronic liver disease worldwide. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) and NAFLD share multiple common risk factors. Life's Crucial 9 (LC9), a novel indicator for comprehensive assessment of cardiovascular health (CVH), has not yet been studied in terms of its association with or predictive value for NAFLD. This study analyzed data from 10,197 participants in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 2007 to 2018. The association between LC9 and NAFLD was assessed using weighted logistic regression, while weighted Cox proportional hazards models were applied to evaluate the relationship between LC9 and all-cause mortality among NAFLD patients. Restricted cubic spline (RCS) analysis was conducted to explore dose-response relationships, and Kaplan-Meier survival curves were utilized to examine differences in survival outcomes. Machine learning (ML) approaches were employed to construct predictive models, with the optimal model further interpreted using SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP). An increase of 10 points in LC9 was negatively associated with the risk of NAFLD (model 3: OR = 0.39, 95% CI = 0.36 - 0.42, P < 0.001) and all-cause mortality in NAFLD patients (model 3: HR = 0.78, 95% CI = 0.67 - 0.91, P < 0.001). A non-linear relationship was observed between LC9 and NAFLD (P < 0.0001 for nonlinearity). Among the eight ML models, the Support Vector Machine (SVM) demonstrated the best predictive performance (AUC = 0.873). SHAP analysis indicated that LC9 was the most significant predictor in the model. LC9 demonstrated a nonlinear negative association with NAFLD and a linear negative association with all-cause mortality in NAFLD patients. Maintaining a higher LC9 score may reduce the risk of NAFLD and all-cause mortality among NAFLD patients. The predictive model developed using Support Vector Machine (SVM) exhibited strong clinical predictive value, with LC9 being the most critical factor in the model, facilitating self-risk assessment and targeted intervention.
Keywords: Life’s Crucial 9; Machine learning; NAFLD; NHANES; SHAP.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval: The present study utilizes publicly accessible data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Given that the utilized data are anonymized and publicly available, ethical approval was not deemed necessary for this research. Consent to participate: This study used publicly available data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). NHANES is a program conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that collects health and nutritional data from a representative sample of the U.S. population. The NHANES data used in this research are de-identified and publicly available, so no individual consent was required for this study. The study was conducted in accordance with ethical standards and institutional guidelines for research using publicly available data.
Figures


References
-
- Riazi, K. et al. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol.7(9), 851–861 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Adams, L. A., Anstee, Q. M., Tilg, H. & Targher, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its relationship with cardiovascular disease and other extrahepatic diseases. Gut66(6), 1138–1153 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Lloyd-Jones, D. M. et al. Defining and setting National goals for cardiovascular health promotion and disease reduction: the American heart association’s strategic impact goal through 2020 and beyond. Circulation121(4), 586–613 (2010). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

