A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence and risk of syphilis among blood donors in Thailand
- PMID: 40102537
- PMCID: PMC11920362
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-94332-3
A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence and risk of syphilis among blood donors in Thailand
Abstract
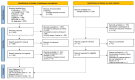
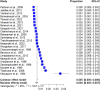
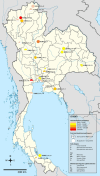
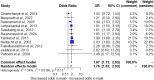
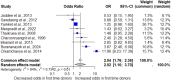
Despite rising rates of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in Thailand, including syphilis, data on its prevalence and associated risk factors among blood donors remain scarce. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to estimate the prevalence of syphilis and identify the key risk factors among blood donors in Thailand to inform targeted interventions for enhanced blood safety.The study protocol was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42024560215) and conducted following PRISMA guidelines. Comprehensive searches were performed across major databases, including ProQuest, Journals@Ovid, Embase, Scopus, PubMed, and MEDLINE, to identify relevant studies. A random-effects model was used to calculate the pooled prevalence and odds ratios (ORs) for syphilis risk factors. Heterogeneity was quantified using the I² statistic, and meta-regression and subgroup analyses were employed to explore potential sources of heterogeneity. Publication bias was assessed using funnel plots and Egger's regression test. A total of 23 studies involving 1,142,910 blood donors were included. The pooled prevalence of syphilis among blood donors in Thailand was 0.42% (95% CI 0.27-0.66%, I²: 99.3%, number of infections: 6,173), with a decreasing trend over time. Male donors were significantly more likely to have syphilis (P < 0.0001; pooled OR: 1.76; 95% CI 1.53-2.03; I²: 34.2%, 651,019 participants). First-time donors also had an elevated risk of syphilis (P = 0.02; pooled OR: 2.02; 95% CI 1.10-3.70; I²: 94.0%, 215,245 participants). Additionally, the analysis revealed a significant association between increasing age and higher syphilis risk among blood donors. The systematic review and meta-analysis indicated that syphilis prevalence among blood donors in Thailand is declining; however, male and first-time donors, as well as older age groups, remain at higher risk. To enhance blood safety, targeted interventions are needed, including refining donor screening questionnaires, expanding educational campaigns for high-risk groups, and incorporating advanced screening technologies. Strengthening and regularly updating national screening policies will ensure the effective mitigation of syphilis transmission among blood donors in Thailand.
Keywords: Blood donors; Meta-analysis; Prevalence; Syphilis; Systematic review; Thailand.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sero-epidemiology and associated factors of HIV, HBV, HCV and syphilis among blood donors in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Aug 9;21(1):778. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06505-w. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34372772 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and factors associated with transfusion-transmissible infections (HIV, HBV, HCV and Syphilis) among blood donors in Gabon: Systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 19;19(8):e0307101. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307101. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39159193 Free PMC article.
-
Sero-prevalence of syphilis and associated factors among pregnant women in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Syst Rev. 2021 Aug 12;10(1):223. doi: 10.1186/s13643-021-01786-3. Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34384495 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and associated factors of HIV among female sex workers in Eastern and Southern Africa: Systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 2;19(12):e0313868. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313868. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39621614 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of HIV/syphilis co-infection among men who have sex with men in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Public Health. 2025 Apr 7;25(1):1297. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-22499-5. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40197258 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nuraini, F. R. & Muflikhah, N. D. Prevalence of syphilis cases among blood donors in Bojonegoro. Jurnal Ilmu Kesehatan Masyarakat13(2), 145–154 (2022).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

