Centrobin serves as a safeguard to guide timely centriole maturation during the cell cycle
- PMID: 40102598
- PMCID: PMC11920255
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-94414-2
Centrobin serves as a safeguard to guide timely centriole maturation during the cell cycle
Abstract
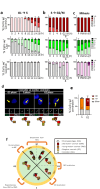
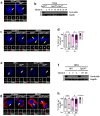
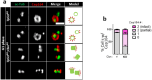
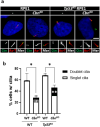
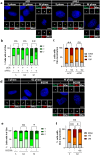
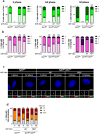
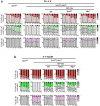
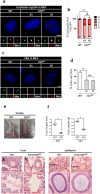
Centrioles assemble and segregate in link to the cell cycle. Daughter centrioles assemble at S phase, and become young mother centrioles after M phase. Since distal appendages (DAs) are installed to young mother centrioles at the second G2/M transition phase, it takes one and a half cell cycle for a daughter centriole to fully mature into an old mother centriole. Here, we investigated specific roles of centrobin on centriole maturation by tracing its centriole localization throughout the cell cycle. Centrobin instantly places at the nascent daughter centrioles during the S phase, maintains its localization through subsequent cell cycle as these daughter centrioles mature into young mother centrioles, and detaches from the young mother centriole during the G2 phase, prior to DA installation. Centrobin KO cells exhibit two DA-installed centrioles, due to premature DA installation in daughter centrioles, and can produce doublet cilia from two DA-installed basal bodies. We also present evidence that direct phosphorylation of Plk1 is crucial for centrobin attachment to centrioles during G2 and M phases. Finally, premature DA installation was also observed in centrobin KO mice. Our results collectively demonstrate that centrobin serves as a safeguard to guide timely centriole maturation during the cell cycle.
Keywords: Cell cycle; Centriole; Centriole maturation; Centrobin; Distal appendage; Plk1; Spermatogenesis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PLK1 controls centriole distal appendage formation and centrobin removal via independent pathways.J Cell Sci. 2022 Apr 15;135(8):jcs259120. doi: 10.1242/jcs.259120. Epub 2022 Apr 21. J Cell Sci. 2022. PMID: 35343570
-
Centrobin-centrosomal protein 4.1-associated protein (CPAP) interaction promotes CPAP localization to the centrioles during centriole duplication.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 30;289(22):15166-78. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.531152. Epub 2014 Apr 3. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24700465 Free PMC article.
-
Centriole reduplication during prolonged interphase requires procentriole maturation governed by Plk1.Curr Biol. 2010 Jul 27;20(14):1277-82. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.05.050. Epub 2010 Jun 17. Curr Biol. 2010. PMID: 20656208 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Polo-like Kinases Plk1 and Plk4 in the Initiation of Centriole Duplication-Impact on Cancer.Cells. 2022 Feb 24;11(5):786. doi: 10.3390/cells11050786. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35269408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The PLK4-STIL-SAS-6 module at the core of centriole duplication.Biochem Soc Trans. 2016 Oct 15;44(5):1253-1263. doi: 10.1042/BST20160116. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016. PMID: 27911707 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

