Recapitulation and reversal of neuropsychiatric phenotypes in a mouse model of human endogenous retrovirus type W expression
- PMID: 40102613
- PMCID: PMC12185329
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-025-02955-9
Recapitulation and reversal of neuropsychiatric phenotypes in a mouse model of human endogenous retrovirus type W expression
Abstract
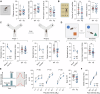
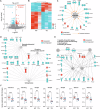
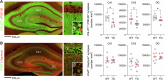
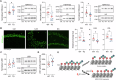
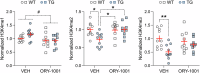
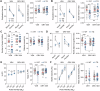
Human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs) are inherited genetic elements derived from exogenous retroviral infections occurring throughout evolution. Accumulating evidence implicates increased expression of HERV type W envelope (HERV-W ENV) in psychiatric and neurodevelopmental disorders. To gain more mechanistic insights into the neurobiological disease pathways affected by HERV-W ENV expression, we took advantage of a mouse model that recapitulates the expression of the human-specific HERV-W ENV protein. Behavioral and cognitive phenotyping of transgenic (TG) mice expressing HERV-W ENV and wild-type (WT) controls showed that expression of this retroviral envelope caused deficits in numerous functional domains, including repetitive behavior, social and object recognition memory, and sensorimotor gating. Genome-wide RNA sequencing of hippocampal tissue demonstrated that transgenic expression of HERV-W ENV led to transcriptomic alterations that are highly relevant for psychiatric and neurodevelopmental disorders, cognitive functions, and synaptic development. Differential gene expression in TG mice encompassed a downregulation of several genes associated with schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorder, including Setd1a, Cacna1g, Ank3, and Shank3, as well as a downregulation of histone methyltransferase genes that belong to the Set1-like histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methyltransferase family (Kmt2a, Kmt2b and Kmt2d). Concomitant to the latter, HERV-W ENV mice displayed increased enzymatic activity of lysine-specific demethylase-1 (LSD1), increased H3K4 mono-methylation, and decreased H3K4 di- and tri-methylation in the hippocampus. Importantly, pharmacological inhibition of LSD1 through oral ORY-1001 treatment normalized abnormal H3K4 methylation and rescued the behavioral and cognitive deficits in HERV-W ENV mice. In conclusion, our study suggests that the expression of HERV-W ENV has the capacity to disrupt various behavioral and cognitive functions and to alter the brain transcriptome in a manner that is highly relevant to neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders. Moreover, our study identified epigenetic pathways that may offer avenues for pharmacological interventions against behavioral and cognitive deficits induced by increased HERW-W expression.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endogenous retroviruses in neurodevelopmental, psychotic and cognitive disorders.Microbes Infect. 2025 Jul-Aug;27(5-6):105479. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2025.105479. Epub 2025 Feb 4. Microbes Infect. 2025. PMID: 39914656 Review.
-
Molecular dissection of HERV-W dependent microglial- and astroglial cell polarization.Microbes Infect. 2025 Jul-Aug;27(5-6):105382. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2024.105382. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Microbes Infect. 2025. PMID: 38944109
-
Transcriptional Upregulation of HERV-env Genes Under Simulated Microgravity.Viruses. 2025 Feb 23;17(3):306. doi: 10.3390/v17030306. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40143237 Free PMC article.
-
Human endogenous retrovirus-K envelope protein is aberrantly expressed in serous ovarian cancer and promotes chemosensitivity via NF-κB/P-glycoprotein pathway inhibition.J Ovarian Res. 2025 Jul 4;18(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s13048-025-01722-2. J Ovarian Res. 2025. PMID: 40616136 Free PMC article.
-
[Epigenetics' implication in autism spectrum disorders: A review].Encephale. 2017 Aug;43(4):374-381. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2016.07.007. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Encephale. 2017. PMID: 27692350 French.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 310030_188524/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Swiss National Science Foundation)
- 310030E_193899/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Swiss National Science Foundation)
- PZ00P3_202149/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Swiss National Science Foundation)
- KU1934/2-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- KU1934/5-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

