A structured coalescent model reveals deep ancestral structure shared by all modern humans
- PMID: 40102687
- PMCID: PMC11985351
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-025-02117-1
A structured coalescent model reveals deep ancestral structure shared by all modern humans
Abstract
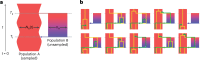
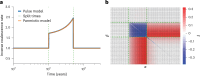
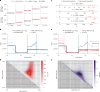
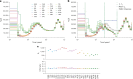
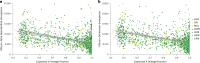
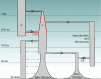
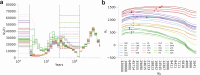
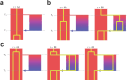
Understanding the history of admixture events and population size changes leading to modern humans is central to human evolutionary genetics. Here we introduce a coalescence-based hidden Markov model, cobraa, that explicitly represents an ancestral population split and rejoin, and demonstrate its application on simulated and real data across multiple species. Using cobraa, we present evidence for an extended period of structure in the history of all modern humans, in which two ancestral populations that diverged ~1.5 million years ago came together in an admixture event ~300 thousand years ago, in a ratio of ~80:20%. Immediately after their divergence, we detect a strong bottleneck in the major ancestral population. We inferred regions of the present-day genome derived from each ancestral population, finding that material from the minority correlates strongly with distance to coding sequence, suggesting it was deleterious against the majority background. Moreover, we found a strong correlation between regions of majority ancestry and human-Neanderthal or human-Denisovan divergence, suggesting the majority population was also ancestral to those archaic humans.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Reich, D. Who we are and how we got here: Ancient DNA and the new science of the human past. Oxford University Press, (2018).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

