Epitranscriptomic regulation of HIF-1: bidirectional regulatory pathways
- PMID: 40102715
- PMCID: PMC11917031
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-025-01149-x
Epitranscriptomic regulation of HIF-1: bidirectional regulatory pathways
Abstract
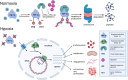
Background: Epitranscriptomics, the study of RNA modifications such as N6-methyladenosine (m6A), provides a novel layer of gene expression regulation with implications for numerous biological processes, including cellular adaptation to hypoxia. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1), a master regulator of the cellular response to low oxygen, plays a critical role in adaptive and pathological processes, including cancer, ischemic heart disease, and metabolic disorders. Recent discoveries accent the dynamic interplay between m6A modifications and HIF-1 signaling, revealing a complex bidirectional regulatory network. While the roles of other RNA modifications in HIF-1 regulation remain largely unexplored, emerging evidence suggests their potential significance.
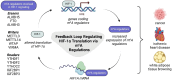
Main body: This review examines the reciprocal regulation between HIF-1 and epitranscriptomic machinery, including m6A writers, readers, and erasers. HIF-1 modulates the expression of key m6A components, while its own mRNA is regulated by m6A modifications, positioning HIF-1 as both a regulator and a target in this system. This interaction enhances our understanding of cellular hypoxic responses and opens avenues for clinical applications in treating conditions like cancer and ischemic heart disease. Promising progress has been made in developing selective inhibitors targeting the m6A-HIF-1 regulatory axis. However, challenges such as off-target effects and the complexity of RNA modification dynamics remain significant barriers to clinical translation.
Conclusion: The intricate interplay between m6A and HIF-1 highlights the critical role of epitranscriptomics in hypoxia-driven processes. Further research into these regulatory networks could drive therapeutic innovation in cancer, ischemic heart disease, and other hypoxia-related conditions. Overcoming challenges in specificity and off-target effects will be essential for realizing the potential of these emerging therapies.
Keywords: Cancer; Epitranscriptomics; HIF-1; Heart; Hypoxia-inducible factor-1; m6A.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Alanova P, et al. HIF-1α limits myocardial infarction by promoting mitophagy in mouse hearts adapted to chronic hypoxia. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2024;240(9):e14202 - PubMed
-
- An S, Shi J, Huang J, Li Z, Feng M, Cao G. HIF-1α-induced upregulation of m6A reader IGF2BP1 facilitates peripheral nerve injury recovery by enhancing SLC7A11 mRNA stabilization. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2023;59(8):596–605. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

