Large indel detection in region-based phased diploid assemblies from linked-reads
- PMID: 40102722
- PMCID: PMC11916464
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-025-11398-z
Large indel detection in region-based phased diploid assemblies from linked-reads
Abstract
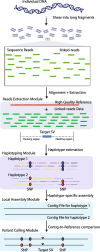
Background: Linked-reads improve de novo assembly, haplotype phasing, structural variant (SV) detection, and other applications through highly-multiplexed genome partitioning and barcoding. Whole genome assembly and assembly-based variant detection based on linked-reads often require intensive computation costs and are not suitable for large population studies. Here we propose an efficient pipeline, RegionIndel, a region-based diploid assembly approach to characterize large indel SVs. This pipeline only focuses on target regions (50kb by default) to extract barcoded reads as input and then integrates a haplotyping algorithm and local assembly to generate phased diploid contiguous sequences (contigs). Finally, it detects variants in the contigs through a pairwise contig-to-reference comparison.
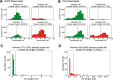
Results: We applied RegionIndel on two linked-reads libraries of sample HG002, one using 10x and the other stLFR. HG002 is a well-studied sample and the Genome in a Bottle (GiaB) community provides a gold standard SV set for it. RegionIndel outperformed several assembly and alignment-based SV callers in our benchmark experiments. After assembling all indel SVs, RegionIndel achieved an overall F1 score of 74.8% in deletions and 61.8% in insertions for 10x linked-reads, and 64.3% in deletions and 36.7% in insertions for stLFR linked-reads, respectively. Furthermore, it achieved an overall genotyping accuracy of 83.6% and 80.8% for 10x and stLFR linked-reads, respectively.
Conclusions: RegionIndel can achieve diploid assembly and detect indel SVs in each target region. The phased diploid contigs can further allow us to investigate indel SVs with nearby linked single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs) and small indels in the same haplotype.
Keywords: Diploid assembly; Linked-reads; Phasing; Region-based; Structural variants.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Code availability and requirements: Project name: RegionIndel Project home page: https://github.com/maiziezhoulab/RegionIndel Operating system(s): Linux Programming language: Python Other requirements: Python 3 or higher. License: The MIT License. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Haplotyping-Assisted Diploid Assembly and Variant Detection with Linked Reads.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2590:161-182. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2819-5_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36335499 Review.
-
Decontamination of DNA sequences from a Streptomyces genome for optimal genome mining.Braz J Microbiol. 2025 Mar;56(1):79-89. doi: 10.1007/s42770-024-01598-2. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Braz J Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39812972
-
Blackbird: structural variant detection using synthetic and low-coverage long-reads.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 18:2024.11.17.624011. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.17.624011. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Bioinform Adv. 2025 Jul 04;5(1):vbaf151. doi: 10.1093/bioadv/vbaf151. PMID: 39605582 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
SAKit: An all-in-one analysis pipeline for identifying novel proteins resulting from variant events at both large and small scales.J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2024 Oct;22(5):2450022. doi: 10.1142/S0219720024500227. Epub 2024 Oct 1. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2024. PMID: 39573833
-
Current Progress in Phased Genome Assembly from Long-Read DNA Sequencing Data.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2955:51-70. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4702-8_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40736893 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

