Survival and risk factor analysis in patients with septic arthritis: a retrospective study of 192 cases
- PMID: 40102780
- PMCID: PMC11916306
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-024-10316-0
Survival and risk factor analysis in patients with septic arthritis: a retrospective study of 192 cases
Abstract
Background: Septic arthritis (SA) presents a complex clinical challenge, often resulting in significant morbidity and mortality. This study aimed to (1) assess overall mortality rates and (2) identify potential factors contributing to increased mortality risk in patients with SA.
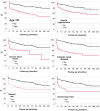
Methods: This retrospective study on SA patients treated at a German university hospital between January 1, 2011, and December 31, 2021. Patients were identified using International Classification of Diseases (ICD)-10 codes for septic arthritis, specifically "M00.-". The study evaluated mortality rates and analyzed comorbidities, pathogens, and other potential risk factors. Kaplan-Meier survival curves and odds ratios (OR) were calculated to assess mortality risk.
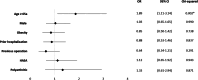
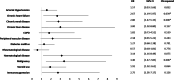
Results: In a cohort of 192 patients diagnosed with SA, 64 patients (33.3%) died during a mean follow-up period of 54.4 ± 42 months. The overall mortality rate was 17.5% at one year, 19.9% at two years, and 28.3% at five years. Patients aged 65 years or older, as well as those with arterial hypertension, congestive heart failure, chronic renal disease, chronic liver disease, malignancy, steroid use and immunosuppression showed significantly higher mortality rates (p < 0.05). Chronic renal disease (OR = 2.80), malignancy (OR = 3.40), and chronic heart failure (OR = 2.62) were identified as significant notably risk factors for mortality.
Conclusion: This study highlights a notably high mortality rate among vulnerable patients with SA, particularly those with pre-existing comorbidities. Recognizing and addressing these risk factors early could improve patient outcomes. These results unterscore the need for close monitoring of SA patients, particularly those with chronic organ conditions, and timely intervention for sepsis to reduce mortality risk.
Keywords: Comorbidities; Complication; Mortality; Septic arthritis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by the Investigational Review Board of University Hospital Regensburg. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Morbimortality in adult patients with septic arthritis: a three-year hospital-based study.BMC Infect Dis. 2016 Jun 1;16:239. doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-1540-0. BMC Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27246346 Free PMC article.
-
Non-gonococcal septic arthritis of native joints in Western Australia. A longitudinal population-based study of frequency, risk factors and outcome.Int J Rheum Dis. 2021 Nov;24(11):1386-1393. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.14221. Epub 2021 Oct 5. Int J Rheum Dis. 2021. PMID: 34609074
-
Septic arthritis in a tertiary care hospital.J Pak Med Assoc. 2006 Mar;56(3):95-8. J Pak Med Assoc. 2006. PMID: 16696505
-
Case Studies and Literature Review of Pneumococcal Septic Arthritis in Adults.Emerg Infect Dis. 2019 Oct;25(10):1824-33. doi: 10.3201/eid2510.181695. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31538930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pneumococcal septic arthritis: review of 190 cases.Clin Infect Dis. 2003 Feb 1;36(3):319-27. doi: 10.1086/345954. Epub 2003 Jan 13. Clin Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 12539074 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of comorbidities on the prognosis of patients with septic arthritis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 18;12:1567229. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1567229. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40606458 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Elsissy JG, Liu JN, Wilton PJ, et al. Bacterial septic arthritis of the adult native knee joint: a review. JBJS Rev. 2020;8:e0059. - PubMed
-
- Margaretten ME, Kohlwes J, Moore D, et al. Does this adult patient have septic arthritis? JAMA. 2007;297:1478–88. - PubMed
-
- Mathews CJ, Kingsley G, Field M, et al. Management of septic arthritis: a systematic review. Postgrad Med J. 2008;84:265–70. - PubMed
-
- García-Arias M, Balsa A, Mola EM. Septic arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2011;25:407–21. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

