The effect of surgery for multipleligament knee injuries on patellar position and patellofemoral function: a retrospective study
- PMID: 40102855
- PMCID: PMC11916915
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-025-05652-z
The effect of surgery for multipleligament knee injuries on patellar position and patellofemoral function: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Patients who undergo reconstruction for multiligament knee injuries (MLKIs) often exhibit knee instability and poor overall knee function during postoperative follow-up. This may be related to the changes in patellar position and decline in patellofemoral function after surgery.
Objective: To evaluate the outcomes following reconstruction of MLKIs through the assessment of: (1) changes in patellar height; (2) anatomical changes in patellofemoral alignment, such as tilt or displacement; and (3) functional outcomes of the patellofemoral joint.
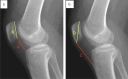
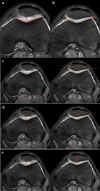
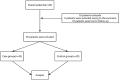
Methods: This retrospective study included 45 patients who underwent reconstruction for MLKIs at our hospital between November 2015 and September 2022, with complete data and meeting the inclusion criteria. These patients formed the case group. An additional 20 outpatients without ligament injuries or patellar dislocation were selected as the normal control group. Patellar height changes in the case group were assessed preoperatively and postoperatively using the Caton-Deschamps (CD) and Insall-Salvati (IS) indices on lateral X-rays. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was used to measure patellofemoral alignment parameters in both groups, including the sulcus angle (SA), patellar tilt angle (PTA), lateral patellofemoral angle (LPA), congruence angle (CA), and patellofemoral index (PI), to evaluate patellofemoral positioning. Additionally, the Kujala score questionnaire was used to assess the stability function of the patellofemoral joint.
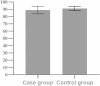
Results: Preoperative patellar height in the case group, measured by the CD and IS indices, was (1.07 ± 0.10, 1.10 ± 0.09), showing a statistically significant difference when compared to postoperative measurements (0.96 ± 0.13, 1.05 ± 0.10) (P < 0.05). However, postoperative patellofemoral alignment parameters, including SA, PTA, LPA, CA, and PI, in the case group showed no statistically significant differences compared to the control group (P > 0.05). At the latest follow-up, the patellofemoral function score in the case group was (89.0 ± 5.3), which was not significantly different from the control group (91.0 ± 2.9) (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: After reconstruction of MLKIs, patellar height decreased but remained within the normal range. Patellofemoral alignment was well-maintained, and patellofemoral function was maintained.
Keywords: Multiligament knee injuries; Patellar height; Patellofemoral function; Patellofemoral position.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Luoyang Orthopedic Hospital, Henan Province. The requirement for informed consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of the study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

