Reunderstanding the classical prescription Banxia Xiexin Decoction: new perspectives from a comprehensive review of clinical research and pharmacological studies
- PMID: 40102869
- PMCID: PMC11921579
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-025-01087-0
Reunderstanding the classical prescription Banxia Xiexin Decoction: new perspectives from a comprehensive review of clinical research and pharmacological studies
Abstract
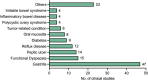
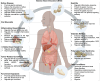
Classical prescriptions of Chinese medicine represent the crystallized wisdom of millennia of clinical practice, enduring as cornerstones of therapeutic intervention due to their demonstrated efficacy across generations. Their evolving role in modern healthcare systems reflects shifting disease patterns, scientific advancements, and global health priorities. Banxia Xiexin Decoction (BXD), formulated by Zhang Zhongjing in the Treatise on Febrile and Miscellaneous Diseases (Shanghanlun), is a time-honored classical prescription renowned for its therapeutic versatility in managing gastrointestinal disorders, both in China and internationally. Recent advancements in clinical research and pharmacological studies on BXD underscore the necessity for a comprehensive bibliometric analysis to summarize and elucidate its specific clinical benefits. Through an extensive literature review of publications from the Web of Science, PubMed, Scopus, and the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) between 1997 and 2024, 11 major categories of clinical applications for BXD were identified, along with an analysis of the potential pharmacological mechanisms, such as chronic gastritis, functional dyspepsia, and inflammatory bowel disease. We believe this review will provide new insights into the understanding of clinical value of BXD and identify potential future perspectives for its research and development.
Keywords: Banxia Xiexin Decoction; Bibliometric analysis; Classical prescription; Gastric ulcer; Gastritis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Zhang C, Liu Y, Li H, Li B, Dong Y, Liu S. Analysis on evolution of clinical application of classic famous prescription Banxia Xiexin Decoction in ancient and modern times. J Basic Chin Med. 2023;29(03):452–6.
-
- Miyano K, Hasegawa S, Asai N, Uzu M, Yatsuoka W, Ueno T, et al. The Japanese herbal medicine Hangeshashinto induces oral keratinocyte migration by mediating the expression of CXCL12 through the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12: 695039. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pharmacopoeia Commission of the People’s Republic of China. The Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Beijing: China Medical Science Press; 2020.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

