A web-based platform for optimizing healthcare resource allocation and workload management using agile methodology and WISN theory
- PMID: 40102889
- PMCID: PMC11916971
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-025-12473-7
A web-based platform for optimizing healthcare resource allocation and workload management using agile methodology and WISN theory
Abstract
Background: Effective healthcare workforce management is critical for ensuring quality care delivery, particularly in resource-constrained settings. The World Health Organization's (WHO) Workload Indicators of Staffing Need (WISN) methodology provides an evidence-based framework for optimizing staffing levels. However, manual implementation of the WISN methodology is labour-intensive, error-prone, and time-consuming. To address these challenges, the Platform for Resource Allocation and Optimization for Healthcare Facilities (PRAYOJN) platform was developed as a web-based tool to automate WISN calculations, streamline data analysis, and improve workforce planning.
Objective: To develop and validate a web-based system that automates the WISN methodology for healthcare workforce planning.
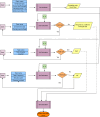
Methods: The PRAYOJN platform was developed using an agile methodology, structured over five iterative sprints. These sprints incorporated stakeholder feedback to refine system functionalities, ensuring adaptability to real-world healthcare needs. The platform integrates data for principal, supporting, and ancillary tasks to calculate staffing requirements. Key functionalities include automated computation of Available Work Time (AWT), Standard Workload (SW), Category Allowance Factor (CAF), and Individual Allowance Factor (IAF). Alpha testing validated usability and accuracy, while beta testing in a clinical phlebotomy department assessed real-world performance.
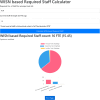
Results: The platform calculated an ideal staffing requirement of 15.53 Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) for the phlebotomy department, aligning closely with the current staff strength of 15 FTE. Agile development ensured iterative improvements, enhancing user interface (UI) and user experience (UX). Feedback highlighted the platform's user-friendly design, with dynamic visualizations such as pie charts and bar graphs aiding workload interpretation. Users praised its efficiency, adaptability, and role in reducing calculation complexity.
Conclusion: PRAYOJN modernizes and enhances WISN-based workforce planning by automating workload calculations, improving data visualization, and supporting real-time decision-making. Its scalability and intuitive interface position it as a valuable tool for optimizing staffing efficiency across diverse healthcare environments.
Keywords: Agile development in healthcare; Healthcare resource allocation; Healthcare workforce optimization; PRAYOJN platform; Staffing automation; Workforce planning tool; Workload indicators of staffing need (WISN).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Since the study was mainly on software designing and the operational study was based on observations and interaction with management team (did not involve human data) the study was exempted from IRB approval by the Institutional Ethical Review Board of the Institute of Health Management Research, Bangalore (IIHMR-B). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Asres GD, Gessesse YK. Workload indicators of staffing need (WISN) method for health workforce planning at health facility: A scoping review. Hum Factors Healthc. 2024;6:100078. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

