Fibroblast IRF7-mediated chondrocyte apoptosis affects the progression of collapse in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head
- PMID: 40102965
- PMCID: PMC11921700
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-025-05557-x
Fibroblast IRF7-mediated chondrocyte apoptosis affects the progression of collapse in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head
Abstract
Purpose: The objective of this study was to identify potential genes implicated in the "peri-collapse" synovium of osteonecrosis of the femoral head through coding gene sequencing and to further clarify their specific mechanisms via in vitro experiments.
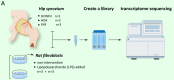
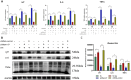
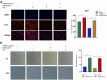
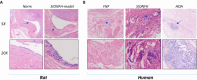
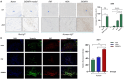
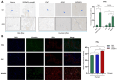
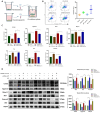
Methods: Steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head (SIONFH) (n = 3), femoral neck fracture (FNF) (n = 3), and hip osteoarthritis (HOA) (n = 3) Synovial tissue of the hip joint was collected in total hip arthroplasty. A cellular model of SIONFH constructed from rat synovial fibroblasts by lipopolysaccharide intervention. Lentiviral technology was used to construct a model for fibroblast knockout of the Irf7 gene. HE was used to compare the characteristics of synovial tissue damage, and immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry were used to compare the expression levels of VIM, IRF7, and IFNα. PCR, WB, and IF were used to examine Irf7 knockdown efficiency, chondrocyte proliferation (Col2a1, Aggrecan, Sox9), cartilage matrix degradation (Mmp13), and apoptosis (Bcl2, Bax, and Caspase3) expression under co-culture conditions. Crystalline violet staining was used to observe the migration rate of fibroblasts, and flow cytometry was used to detect the apoptosis level of chondrocytes under co-culture conditions.
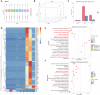
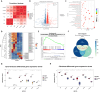
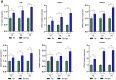
Results: Transcriptome sequencing of synovial tissue and fibroblasts ultimately screened for six differential genes, HOOK1, RNPC3, KCNA3, CD48, IRF7, SAMD9. Compared to FNF and HOA, synovial inflammatory cell recruitment and synovial hyperplasia were more pronounced in SIONFH. IF and IHC confirmed high expression of IRF7 and IFNα in the synovium of SIONFH. PCR and WB results suggested that fibroblasts highly expressed Irf7, Hook1, Rnpc3, Kcna3, Cd48, Samd9, Il-6, and Tnfα after lipopolysaccharide intervention, and the expression levels of Il-6 and Tnfα were significantly reduced after knockdown of Irf7 (P < 0.001). In the co-culture system, fibroblasts intervened with lipopolysaccharide significantly promoted chondrocyte apoptosis, the rate of cartilage matrix degradation, while inhibiting the level of chondrocyte proliferation, and this result was significantly reversed in Irf7 knockout fibroblasts. This was supported by flow cytometry results.
Conclusions: IRF7, HOOK1, RNPC3, KCNA3, CD48, and SAMD9 as potential genes affecting the progression of SIONFH collapse. Irf7 mediates the fibroblast inflammatory response and affects the collapse process of SIONFH by influencing chondrocyte apoptosis. Thus, intervention in IRF7 holds promise as one of the key targets for reversing the collapse process of SIONFH.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Collapse; Gene expression profiles; Steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head; Synovial fibroblasts.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the board of research ethics in The Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (Approval No. PJ-XS-20230523-002). All patients give informed consent. Consent for publication: All authors of this manuscript agree with the views expressed in this article and consent to publication. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CircPVT1 up-regulation attenuates steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head through regulating miR-21-5p-mediated Smad7/TGFβ signalling pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 May;25(10):4608-4622. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16294. Epub 2021 Mar 18. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33733589 Free PMC article.
-
HIF-1-Dependent IL-6 Activation in Articular Chondrocytes Initiating Synovitis in Femoral Head Ischemic Osteonecrosis.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016 Jul 6;98(13):1122-31. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.15.01209. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016. PMID: 27385686
-
Integrated bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation of exosome-related gene signature in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Jan 9;20(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05456-1. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 39789578 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 is a positive regulator of Sox9 activity in femoral head osteonecrosis.Bone. 2011 Mar 1;48(3):507-13. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2010.10.006. Epub 2010 Oct 13. Bone. 2011. PMID: 20950722
-
Synovial microenvironment in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: crosstalk with chondrocytes and potential therapeutic targets.Life Sci. 2024 Oct 1;354:122947. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122947. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39117138 Review.
References
-
- Cui Q, Jo WL, Koo KH, Cheng EY, Drescher W, Goodman SB, Ha YC, Hernigou P, Jones LC, Kim SY, Lee KS, Lee MS, Lee YJ, Mont MA, Sugano N, Taliaferro J, Yamamoto T, Zhao D. Arco consensus on the pathogenesis of non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36:e65. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82274544/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82004392/National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Science Foundation
- 20223012/Key Projects of Guangdong Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- XGS 2023008/NATCM' s Project of High-level Construction of Key TCM Disciplines (Traditional Chinese Orthopedics); Traditional Chinese Orthopedics Open subject of FTCM
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

