Survival after standard or oncoplastic breast-conserving surgery versus mastectomy for breast cancer
- PMID: 40103401
- PMCID: PMC11920510
- DOI: 10.1093/bjsopen/zraf002
Survival after standard or oncoplastic breast-conserving surgery versus mastectomy for breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Recent evidence suggests a survival advantage after breast-conserving surgery compared with mastectomy. Previous studies have compared survival outcomes after standard breast-conserving surgery, but no studies have compared survival outcomes after oncoplastic breast-conserving surgery. The aim of this study was to compare survival outcomes after breast-conserving surgery + radiotherapy (and an oncoplastic breast-conserving surgery + radiotherapy subgroup) with those after mastectomy ± radiotherapy.
Methods: Patients diagnosed with primary invasive breast cancer between 1 January 2010 and 31 December 2019 were identified from a prospectively maintained National Cancer Registry. Overall survival and breast cancer-specific survival outcomes were analysed using Kaplan-Meier analysis and Cox regression analysis adjusting for patient demographics, tumour characteristics, and treatment adjuncts.
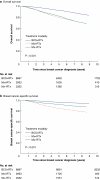
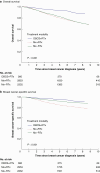
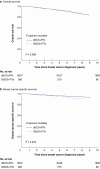
Results: A total of 14 182 patients were eligible (8537 patients underwent standard breast-conserving surgery + radiotherapy, 360 patients underwent oncoplastic breast-conserving surgery + radiotherapy, 2953 patients underwent mastectomy + radiotherapy, and 2332 patients underwent mastectomy - radiotherapy). The median follow-up was 7.27 (range 0.2-13.6) years. Superior 10-year survival was observed after breast-conserving surgery + radiotherapy (overall survival: 81.2%; breast cancer-specific survival: 93.3%) compared with mastectomy + radiotherapy (overall survival: 63.4%; breast cancer-specific survival: 75.9%) and mastectomy - radiotherapy (overall survival: 63.1%; breast cancer-specific survival: 87.5%). Ten-year overall survival and breast cancer-specific survival after oncoplastic breast-conserving surgery + radiotherapy were 86.1% and 90.2% respectively. After adjusted analysis, breast-conserving surgery + radiotherapy was associated with superior survival outcomes compared with mastectomy + radiotherapy (overall survival: HR 1.34 (95% c.i. 1.20 to 1.51); breast cancer-specific survival: HR 1.62 (95% c.i. 1.38 to 1.90)) and mastectomy - radiotherapy (overall survival: HR 1.57 (95% c.i. 1.41 to 1.75); breast cancer-specific survival: HR 1.70 (95% c.i. 1.41 to 2.05)). Similar survival outcomes were observed amongst patients treated with oncoplastic breast-conserving surgery + radiotherapy compared with mastectomy + radiotherapy (overall survival: HR 1.72 (95% c.i. 1.62 to 2.55); breast cancer-specific survival: HR 1.74 (95% c.i. 1.06 to 2.86)) and mastectomy - radiotherapy (overall survival: HR 2.21 (95% c.i. 1.49 to 3.27); breast cancer-specific survival: HR 1.89 (95% c.i. 1.13 to 3.14)).
Conclusion: Breast-conserving surgery + radiotherapy and oncoplastic breast-conserving surgery + radiotherapy are associated with superior overall survival and breast cancer-specific survival compared with mastectomy ± radiotherapy. The findings should inform discussion of surgical treatment options for patients with breast cancer.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of BJS Foundation Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Cancer Research UK . Breast Cancer Statistics. 2023. https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/s... (accessed 23 January 2024)
-
- Fisher B, Montague E, Redmond C, Barton B, Borland D, Fisher ER et al. Comparison of radical mastectomy with alternative treatments for primary breast cancer. A first report of results from a prospective randomized clinical trial. Cancer 1977;39:2827–2839 - PubMed
-
- Fisher B, Bauer M, Margolese R, Poisson R, Pilch Y, Redmond C et al. Five-year results of a randomized clinical trial comparing total mastectomy and segmental mastectomy with or without radiation in the treatment of breast cancer. N Eng J Med 1985;312:665–673 - PubMed
-
- Veronesi U, Cascinelli N, Mariani L, Greco M, Saccozzi R, Luini A et al. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized study comparing breast-conserving surgery with radical mastectomy for early breast cancer. N Eng J Med 2002;347:1227–1232 - PubMed
-
- Fisher B, Anderson S, Bryant J, Margolese RG, Deutsch M, Fisher ER et al. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing total mastectomy, lumpectomy, and lumpectomy plus irradiation for the treatment of invasive breast cancer. N Eng J Med 2002;347:1233–1241 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

