Prognostic Significance of +1q Alterations in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma Treated With Daratumumab-, Elotuzumab-, and Carfilzomib-Based Triplet Regimens: A Multicenter Real-World Analysis of 635 Patients
- PMID: 40103518
- PMCID: PMC12134713
- DOI: 10.1111/ejh.14413
Prognostic Significance of +1q Alterations in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma Treated With Daratumumab-, Elotuzumab-, and Carfilzomib-Based Triplet Regimens: A Multicenter Real-World Analysis of 635 Patients
Abstract
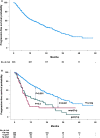
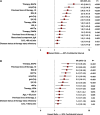
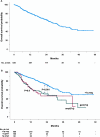
Relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) research on the impact of +1q abnormalities in real-world settings is limited. This study evaluated the prognostic and predictive significance of 1q gain [gain(1q)] and amplification [ampl(1q)] in 635 RRMM patients treated with daratumumab-, elotuzumab-, and carfilzomib-based triplet regimens. Patients with +1q abnormalities had lower deep response rates [≥ CR: 9.4% for gain(1q), 11.6% for ampl(1q)] versus 20.2% in +1q-negative patients. Multivariable ordinal logistic analysis showed significantly lower odds of achieving ≥ CR in patients with gain(1q) (OR = 0.49, p < 0.001) or ampl(1q) (OR = 0.58, p = 0.0037). Progression-free survival (PFS) was longer in +1q-negative patients (28 months) compared to those with gain(1q) (8 months) or ampl(1q) (7.4 months). Multivariable models identified gain(1q) (HR = 1.9, p < 0.001) and ampl(1q) (HR = 2.2, p < 0.001) as independent negative prognostic factors alongside del17p, t(4;14), creatinine clearance < 60 mL/min, and ISS Stages II and III. Similarly, overall survival (OS) was reduced for patients with gain(1q) (25 months) and ampl(1q) (19.5 months) versus 42.2 months in +1q-negative patients. Multivariable analysis showed gain(1q) (HR = 1.6, p = 0.007) and ampl(1q) (HR = 2.0, p = 0.002) as independent predictors of increased mortality. Ancillary +1q abnormalities associated with high-risk cytogenetic changes were linked to both shorter PFS and OS. Stratification into no-hit, single-hit, double-hit, and triple-hit groups showed significant survival differences, emphasizing the impact of cumulative cytogenetic abnormalities on outcomes. In conclusion, +1q abnormalities significantly impact prognosis in RRMM and should be considered in risk stratification. The study emphasizes the importance of comprehensive cytogenetic profiling in real-world settings and highlights the need for personalized treatment strategies to improve patient outcomes.
Keywords: +1q alterations and prognosis in RRMM 1q abnormalities; DaraRd; EloPd; EloRd; KRd; RRMM.
© 2025 The Author(s). European Journal of Haematology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bruzzese A., Derudas D., Galli M., et al., “Elotuzumab Plus Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma: Extended 3‐Year Follow‐Up of a Multicenter, Retrospective Clinical Experience With 319 Cases Outside of Controlled Clinical Trials,” Hematological Oncology 40, no. 4 (2022): 704–715. - PubMed
-
- Martino E. A., Conticello C., Zamagni E., et al., “Carfilzomib Combined With Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone (KRd) as Salvage Therapy for Multiple Myeloma Patients: Italian, Multicenter, Retrospective Clinical Experience With 600 Cases Outside of Controlled Clinical Trials,” Hematological Oncology 40, no. 5 (2022): 1009–1019. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

