Berberine and its derivatives: mechanisms of action in myocardial vascular endothelial injury - a review
- PMID: 40103596
- PMCID: PMC11914797
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1543697
Berberine and its derivatives: mechanisms of action in myocardial vascular endothelial injury - a review
Abstract
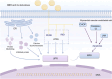
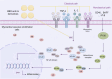
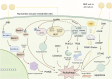
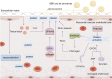
Myocardial vascular endothelial injury serves as a crucial inducer of cardiovascular diseases. Mechanisms such as endoplasmic reticulum stress, apoptosis, inflammation, oxidative stress, autophagy, platelet dysfunction, and gut microbiota imbalance are intimately linked to this condition. Berberine and its derivatives have demonstrated potential in modulating these mechanisms. This article reviews the pathogenesis of endothelial injury in myocardial vessels, the pharmacological effects of berberine and its derivatives, particularly their interactions with targets implicated in vascular endothelial injury. Furthermore, it discusses clinical applications, methods to enhance bioavailability, and toxicity concerns, aiming to lay a foundation for the development of BBR as a therapeutic agent for cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: berberine; cardioprotection; cardiovascular diseases; mechanism of action; myocardial vascular endothelial injury.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Guo, Dou, Zhang, Shi, Zhang, Zhang, Lan and Su.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


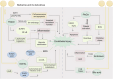
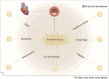
Similar articles
-
Berberine ameliorates vascular dysfunction by downregulating TMAO-endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway via gut microbiota in hypertension.Microbiol Res. 2024 Oct;287:127824. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2024.127824. Epub 2024 Jul 20. Microbiol Res. 2024. PMID: 39053076
-
Berberine prevents against myocardial injury induced by acute β-adrenergic overactivation in rats.J Appl Toxicol. 2024 Nov;44(11):1700-1713. doi: 10.1002/jat.4659. Epub 2024 Jul 9. J Appl Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38981847
-
Berberine protects rat heart from ischemia/reperfusion injury via activating JAK2/STAT3 signaling and attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016 Mar;37(3):354-67. doi: 10.1038/aps.2015.136. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016. PMID: 26806299 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between gut microbiota and berberine, a necessary procedure to understand the mechanisms of berberine.J Pharm Anal. 2022 Aug;12(4):541-555. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2021.10.003. Epub 2021 Oct 21. J Pharm Anal. 2022. PMID: 36105164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atheroprotective Effects and Molecular Mechanism of Berberine.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Nov 16;8:762673. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.762673. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34869592 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Berberine nanoemulsion attenuates bisphenol A-induced metabolic impairment through NF-κB signaling in the liver of rat.Toxicol Rep. 2025 Jun 17;15:102069. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2025.102069. eCollection 2025 Dec. Toxicol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40687893 Free PMC article.
-
Natural products for intervertebral disc degeneration: mechanistic insights and therapeutic potentials.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 25;16:1605764. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1605764. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40786036 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alamgeer C. P., Akhtar M. S., Jabeen Q., Delecolle J., Heintz D., Garo E., et al. (2016). Endothelium-independent vasorelaxant effect of a Berberis orthobotrys root extract via inhibition of phosphodiesterases in the porcine coronary artery. Phytomedicine 23 (8), 793–799. 10.1016/j.phymed.2016.04.005 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bandala C., Carro-Rodríguez J., Cárdenas-Rodríguez N., Peña-Montero I., Gómez-López M., Hernández-Roldán A. P., et al. (2024). Comparative effects of gymnema sylvestre and berberine on adipokines, body composition, and metabolic parameters in obese patients: a randomized study. Nutrients 16 (14), 2284. 10.3390/nu16142284 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bannerman D. D., Goldblum S. E. (1999). Direct effects of endotoxin on the endothelium: barrier function and injury. Lab. Invest 79 (10), 1181–1199. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

