True AP imaging during lumbar medial branch radiofrequency neurotomy: A technical note
- PMID: 40103656
- PMCID: PMC11919405
- DOI: 10.1016/j.inpm.2025.100558
True AP imaging during lumbar medial branch radiofrequency neurotomy: A technical note
Abstract
Background: Optimal outcomes following lumbar medial branch radiofrequency neurotomy (LMBRFN) require close and parallel electrode placement to the targeted medial branch. True segmental fluoroscopic imaging is critical for LMBRFN performance. A true lateral imaging technique for LMBRFN has been described, and its interobserver reliability has been established. However, a similarly detailed technique for true AP imaging has yet to be proposed.
Objective: This technical note proposes a clear and concise true AP imaging technique for LMBRFN.
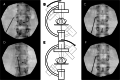
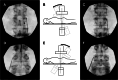
Technique: True AP lumbar imaging involves viewing the spinous process in the midline or midway between the pedicles and aligning cortical bone to create a sharp, superior endplate image. Maneuvering the fluoroscope can produce true AP imaging if the initial AP image is untrue. Oblique (axial plane) fluoroscopic rotation allows the spinous process to be positioned appropriately in the midline. Right versus left oblique rotation is informed by the position of the spinous process relative to the midline. Tilt (longitudinal plane) fluoroscopic rotation produces a sharp superior endplate. Cranial versus caudal tilt is informed by the pedicles' position relative to the vertebral body's upper zone.
Conclusions: When combined with true lateral imaging, the currently proposed AP imaging technique may yield reliable true segmental imaging during LMBRFN. This true AP segmental imaging process may also be applied to other lumbar spine procedures.
Keywords: Lumbar medial branch radiofrequency neurotomy; True AP imaging.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
True lateral imaging during lumbar medial branch radiofrequency neurotomy: Interobserver reliability.Interv Pain Med. 2024 May 14;3(2):100413. doi: 10.1016/j.inpm.2024.100413. eCollection 2024 Jun. Interv Pain Med. 2024. PMID: 39238589 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of Needle Angles for Traditional Lumbar Medial Branch Radiofrequency Ablation: An Osteological Study.Pain Med. 2023 May 2;24(5):488-495. doi: 10.1093/pm/pnac160. Pain Med. 2023. PMID: 36308462
-
The efficacy of repeated radiofrequency medial branch neurotomy for lumbar facet syndrome.J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010 Sep;48(3):240-3. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2010.48.3.240. Epub 2010 Sep 30. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010. PMID: 21082052 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Review of the Effectiveness of Lumbar Medial Branch Thermal Radiofrequency Neurotomy, Stratified for Diagnostic Methods and Procedural Technique.Pain Med. 2020 Jun 1;21(6):1122-1141. doi: 10.1093/pm/pnz349. Pain Med. 2020. PMID: 32040149
-
A narrative review of lumbar medial branch neurotomy for the treatment of back pain.Pain Med. 2009 Sep;10(6):1035-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4637.2009.00692.x. Epub 2009 Aug 18. Pain Med. 2009. PMID: 19694977 Review.
References
-
- Bogduk N., editor. Practice guidelines for spinal diagnostic and treatment procedures. Second ed. San Francisco: International Spine Intervention. Society; 2013.
-
- Schneider B.J., Doan L., Maes M.K., Martinez K.R., Gonzalez Cota A., Bogduk N., Standards Division of the Spine Intervention Society Systematic review of the effectiveness of lumbar medial branch thermal radiofrequency neurotomy, stratified for diagnostic methods and procedural technique. Pain Med. 2020 Jun 1;21(6):1122–1141. doi: 10.1093/pm/pnz349. PMID: 32040149. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Maus T.P., Cohen I., McCormick Z.L., Schneider B.J., Smith C.C., Stojanovic M.P., Waring P.H. Technical manual and atlas of interventional pain and spine procedures. International Pain and Spine Intervention Society; 2024.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources