MicroRNAs modulate CaMKIIα/SIRT1 signaling pathway as a biomarker of cognitive ability in adolescents
- PMID: 40103671
- PMCID: PMC11919301
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbih.2025.100970
MicroRNAs modulate CaMKIIα/SIRT1 signaling pathway as a biomarker of cognitive ability in adolescents
Abstract
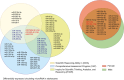
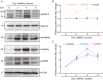
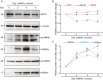
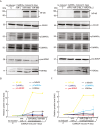
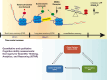
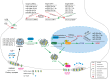
The dynamic regulation of synaptic plasticity underlies memory formation, involving intricate signaling pathways with both facilitatory and inhibitory roles. MicroRNAs are emerging modulators of memory processes through their fine-tuning of gene expression. To explore the influence of miRNAs on adolescent cognitive function, we investigated the association between academic performance, cognitive ability as measured by the Inquiry for Scientific Thinking, Analytics, and Reasoning test, and plasma miRNA profiling in 486 senior high school students. Our analysis identified 38 differentially expressed miRNAs between students with high and low academic performance. Notably, miR-219 b/548e/628/885 and miR-30a/30c-1/195/204 potentially targeted genes associated with the CaMKII/SIRT1 signaling pathway, a crucial facilitator of memory consolidation. Collectively, our findings suggest that specific plasma miRNAs, particularly the CaMKII/SIRT1-related miR-30a/30c-1/195/204 cluster, potentially serve as promising biomarkers for cognitive function in adolescents. Our findings further support the proposed interaction between NF-kB activity and CaMKIIα in regulating synaptic plasticity. Under hypomethylation conditions, increased NF-kB activity, a key component of inflammation and neural plasticity, influences learning and memory. This biological pathway, representing the initiation of epigenetic memory, demonstrates significant predictive power for both cognitive ability and academic performance.
Keywords: Adolescents; CaMKIIα/SIRT1 signaling pathway; Cognitive ability; NF-kB; miRNA.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Teaser: MicroRNAs could be the key to unlocking adolescent cognitive potential.
Figures
References
-
- Bahlakeh G., Gorji A., Soltani H., Ghadiri T. MicroRNA alterations in neuropathologic cognitive disorders with an emphasis on dementia: lessons from animal models. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021;236:806–823. - PubMed
-
- Bao L., Koenig K., Xiao Y., Fritchman J., Zhou S., Chen C. Theoretical model and quantitative assessment of scientific thinking and reasoning. Physical Review Physics Education Research. 2022;18
-
- Barter J.D., Foster T.C. Aging in the brain: new roles of epigenetics in cognitive decline. Neuroscientist : a review journal bringing neurobiology, neurology and psychiatry. 2018;24:516–525. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

